Scientists Grow Cartilage to Reconstruct Nose
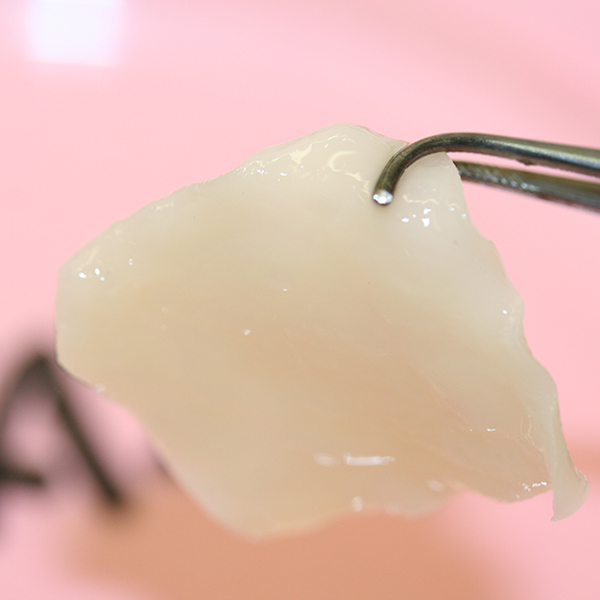
Made from a probe of the nasal septum: white, glossy cartilage made in the laboratory (Figure: Department of Biomedicine at the University of Basel)
A research team from the University of Basel in Switzerland has reported that nasal reconstruction using engineered cartilage is possible. They used a method called tissue engineering where cartilage is grown from patients’ own cells.
This new technique was applied on five patients, aged 76 to 88 years, with severe defects on their nose after skin cancer surgery. One year after the reconstruction, all five patients were satisfied with their ability to breathe as well as with the cosmetic appearance of their nose. None of them reported any side effects.
Cells from the nasal septum
The type of non-melanoma skin cancer investigated in this study is most common on the nose, specifically the alar wing of the nose, because of its cumulative exposure to sunlight. To remove the tumor completely, surgeons often have to cut away parts of cartilage as well.
Usually, grafts for reconstruction are taken from the nasal septum, the ear or the ribs and used to functionally reconstruct the nose. However, this procedure is very invasive, painful and can, due to the additional surgery, lead to complications at the site of the excision.
Together with colleagues from the University Hospital, the research team from the Department of Biomedicine at the University of Basel has now developed an alternative approach using engineered cartilage tissue grown from cells of the patients’ nasal septum. They extracted a small biopsy, isolated the cartilage cells (chondrocytes) and multiplied them.
The expanded cells were seeded onto a collagen membrane and cultured for two additional weeks, generating cartilage 40 times the size of the original biopsy. The engineered grafts were then shaped according to the defect on the nostril and implanted.
New possibilities for facial reconstruction
According to Ivan Martin, Professor for Tissue Engineering at the Department of Biomedicine at the University and University Hospital of Basel, “The engineered cartilage had clinical results comparable to the current standard surgery. This new technique could help the body to accept the new tissue better and to improve the stability and functionality of the nostril.
Our success is based on the long-standing, effective integration in Basel between our experimental group at the Department of Biomedicine and the surgical disciplines at the University Hospital. The method opens the way to using engineered cartilage for more challenging reconstructions in facial surgery such as the complete nose, eyelid or ear.”
The same engineered grafts are currently being tested in a parallel study for articular cartilage repair in the knee. Despite the optimistic perspectives, the use of these procedures in the clinical practice is still rather distant. “We need rigorous assessment of efficacy on larger cohorts of patients and the development of business models and manufacturing paradigms that will guarantee cost-effectiveness”, says Martin.
Original source
Ilario Fulco, Sylvie Miot, Martin D Haug, Andrea Barbero, Anke Wixmerten, Sandra Feliciano, Francine Wolf, Gernot Jundt, Anna Marsano, Jian Farhadi, Michael Heberer, Marcel Jakob, Dirk J Schaefer, Ivan Martin
Engineered autologous cartilage tissue for nasal reconstruction after tumour resection: an observational first-in-human trial
The Lancet
Further information
Prof. Dr. Ivan Martin, Department of Biomedicine at the University and University Hospital Basel, phone: +41 (0)61 265 23 84, email: ivan.martin@unibas.ch
Anke Wixmerten, Department of Biomedicine at the University and University Hospital Basel, phone: +41 (0)61 328 73 76, E-Mail: anke.wixmerten@usb.ch
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.unibas.chAll latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Superradiant atoms could push the boundaries of how precisely time can be measured
Superradiant atoms can help us measure time more precisely than ever. In a new study, researchers from the University of Copenhagen present a new method for measuring the time interval,…

Ion thermoelectric conversion devices for near room temperature
The electrode sheet of the thermoelectric device consists of ionic hydrogel, which is sandwiched between the electrodes to form, and the Prussian blue on the electrode undergoes a redox reaction…

Zap Energy achieves 37-million-degree temperatures in a compact device
New publication reports record electron temperatures for a small-scale, sheared-flow-stabilized Z-pinch fusion device. In the nine decades since humans first produced fusion reactions, only a few fusion technologies have demonstrated…





















