Sall4 Is Required for DNA Repair in Stem Cells
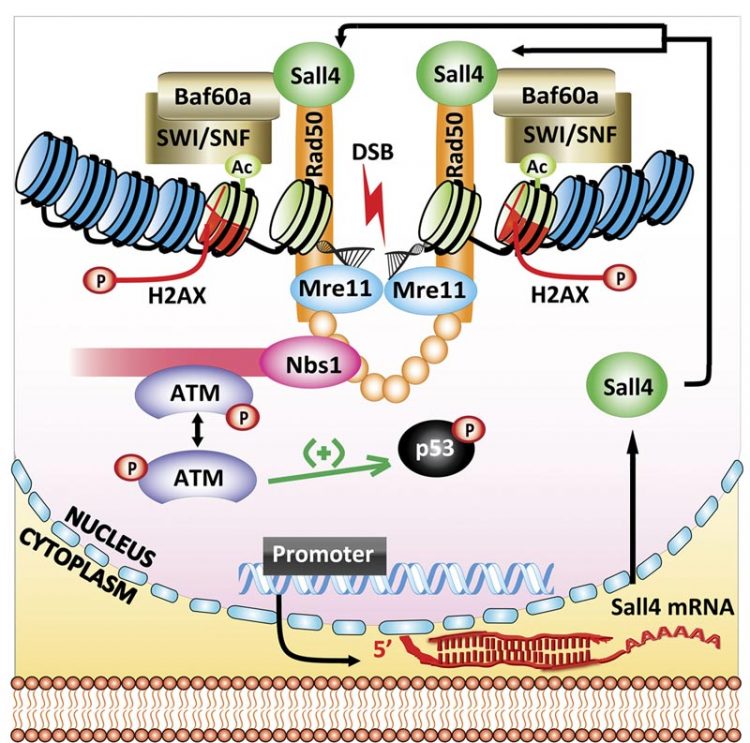
Xiong et al., 2015 Illustrated model for the role of Sall4 in activating ATM to repair DNA damage in embryonic stem cells.
Fixing broken DNA is particularly important for ESCs because they will pass on any mutations to their differentiated descendants. Mouse ESCs are adept at making repairs—they carry far fewer mutations than do differentiated cells—but how they achieve this isn’t clear.
A team of researchers led by Yang Xu, from the University of California, San Diego, tested whether the protein Sall4, which suppresses differentiation of ESCs, has a role in DNA repair.
The researchers found that ESCs lacking Sall4 were poor at mending double-strand breaks, a hazardous form of DNA damage in which both strands of the double helix are severed. They also observed that, after inducing DNA damage in mouse ESCs, Sall4 associated with proteins known to be involved in DNA repair.
Overall, their findings support a model for how Sall4 is recruited to the sites of these breaks and activates ATM, a kinase that signals DNA damage and instigates repair. Because tumor cells often overexpress Sall4, the protein might similarly help them repair DNA damage. Sall4 could therefore be considered a target for drug development in cancer biology.
Xiong, J., et al. 2015. J. Cell Biol. doi:10.1083/jcb.201408106
About The Journal of Cell Biology
The Journal of Cell Biology (JCB) is published by The Rockefeller University Press. All editorial decisions on manuscripts submitted are made by active scientists in conjunction with our in-house scientific editors. JCB content is posted to PubMed Central, where it is available to the public for free six months after publication. Authors retain copyright of their published works, and third parties may reuse the content for non-commercial purposes under a creative commons license.
For more information, please visit www.jcb.org
Contact Information
Rita Sullivan King
Communications Manager
news@rupress.org
Phone: 212-327-8603
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Superradiant atoms could push the boundaries of how precisely time can be measured
Superradiant atoms can help us measure time more precisely than ever. In a new study, researchers from the University of Copenhagen present a new method for measuring the time interval,…

Ion thermoelectric conversion devices for near room temperature
The electrode sheet of the thermoelectric device consists of ionic hydrogel, which is sandwiched between the electrodes to form, and the Prussian blue on the electrode undergoes a redox reaction…

Zap Energy achieves 37-million-degree temperatures in a compact device
New publication reports record electron temperatures for a small-scale, sheared-flow-stabilized Z-pinch fusion device. In the nine decades since humans first produced fusion reactions, only a few fusion technologies have demonstrated…





















