Research paves way for new generation of fungicides
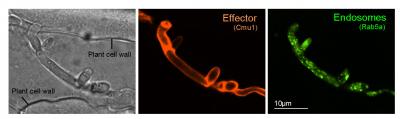
Effector proteins enable the fungi to escape the plant's immune system and allow the fungal cells to enter the plant unrecognized. Credit: University of Exeter
Exeter scientists have now shown that signalling organelles, known as 'early endosomes' act as long distance messengers in the fungi. They travel rapidly along long tube-like cells between the plant-invading fungal cell tip and the fungal cell nucleus.
This rapid communication between the point of invasion and the fungal cell nucleus enables the fungus to produce the effector proteins that help evade the plant's immune response from the moment the fungus enters the host tissue.
This signalling mechanism occurs very early in the fungal infection process, at a time when the fungi are most accessible to fungicide treatment. Disabling the process could result in a new generation of fungicides that are able to act before the fungus has damaged the plant.
Professor Gero Steinberg from the University of Exeter said: “Pathogenic fungi are a major threat to our food security – they can devastate crops and cost billions of pounds worth of damage. In fact, losses of wheat, rice, and maize to fungal pathogens, per year, are the same as the annual spend by US Department of Homeland Security – some 60 billion US dollars.
As fast growing microbes, fungi adapt rapidly to anti-fungal treatments and so we need to develop new fungicides all the time. Our research has led to a better understanding of the mechanisms by which the intruder attacks and overcomes the plant defence. In order to efficiently protect crops, we must better understand molecular mechanisms like these that occur in the very earliest stages of infection.”
Speaking about the research, Deputy Vice Chancellor, Professor Nick Talbot said “The University of Exeter is committed to tackling fundamental research questions to help control plant diseases, which threaten our food supply. We have built a very strong team of researchers studying fungal biology and plant pathology. This exciting discovery by Prof Steinberg's group provides a new potential route to disease control.”
###
The research was supported by the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council.
The paper, 'Long-distance endosome trafficking drives fungal effector production during plant infection', is published in the journal Nature Communications.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.exeter.ac.ukAll latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Superradiant atoms could push the boundaries of how precisely time can be measured
Superradiant atoms can help us measure time more precisely than ever. In a new study, researchers from the University of Copenhagen present a new method for measuring the time interval,…

Ion thermoelectric conversion devices for near room temperature
The electrode sheet of the thermoelectric device consists of ionic hydrogel, which is sandwiched between the electrodes to form, and the Prussian blue on the electrode undergoes a redox reaction…

Zap Energy achieves 37-million-degree temperatures in a compact device
New publication reports record electron temperatures for a small-scale, sheared-flow-stabilized Z-pinch fusion device. In the nine decades since humans first produced fusion reactions, only a few fusion technologies have demonstrated…





















