Mining biotech’s data mother lode
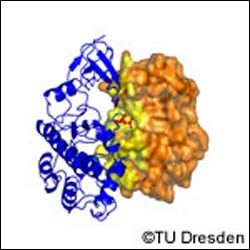
A 3D structure of a kinase-inhibitor interaction predicted for the pancreas tumour gene expression data. The predicted interaction is important for the regulation of cell growth.
A EU-sponsored project has developed a suite of tools that will enable biotech companies to mine through vast quantities of data created by modern life-science labs to find the nuggets of genetic gold that lie within.
The BioGrid project brought together six partners from the UK, Germany, Cyprus and The Netherlands to address one of the key problems facing the life sciences today.
“How to integrate the huge volume of disparate data – on gene expression, protein interactions and the vast output of literature both inside and outside laboratories – to find out what is important,” says Dr Michael Schroeder, Professor of the Bioinformatics group at Dresden Technical University and coordinator of this IST-funded project. “I attended a workshop recently, held by the W3 consortium, and many of the companies there said that this was the biggest problem they face.”
Currently, pharmaceutical and biotech companies produce vast quantities of raw data on the problems that interests them. Microarrays process thousands of samples to discover what genes are over expressing. These over-expressing genes – numbering sometimes in their thousands, too – create proteins. The researchers then need to discover what protein interactions are taking place among all the different proteins created by the over-expressing genes. This is not trivial.
If a researcher can identify protein interactions they then need to do a search on their company intranet to see what other work company labs have produced relevant to the topic. Finally, the researcher must perform a search of academic journals to find relevant journal papers. Currently PubMed, the most important public literature database available, has 15,000,000 entries, and the number is growing every day. Finding relevant data there is again not a trivial task.
Dr Schroeder gives an example. “The medical faculty here were studying pancreatic tumours. They found 1,000 genes over expressing. Using our software they were able to find, among others, three protein interactions that were particularly relevant. Using our literature search ontology they were able to discover that two of these interactions were novel. They are now going to study these novel interactions more closely,” he says.
BioGrid explained
This is how the project will help companies integrate all the data they need to make relevant discoveries using a BioGrid. A BioGrid is essentially a data and computational Grid created through a suite of tools developed by the project.
Here’s how it works. One element of the software suite analyses over-expressing genes discovered during micro assays to establish what proteins become encoded. This uses standard techniques.A second analysis tool in the suite predicts what possible protein-protein interactions are taking place. This is novel. When a gene encodes a protein, the protein folds up into a unique shape, forming a 3D structure. This structure can only interact, or fit, with some proteins, but not others, like pieces of a jigsaw puzzle.
BioGrid’s protein interaction software includes a database of the 20,000 known protein structures and uses that database to identify which ones could potentially interact, among the thousands of proteins created by the over-expressing genes. Once interesting potential protein interactions are known, BioGrid’s ontology-based search technology can mine company or journal data for any relevant information.
Linking all these software tools together is a rules-based Java scripting language called Prova, also developed by the BioGrid team. It is the glue the sticks the Gene Expression, Protein Interaction and ontology-based literature analysis together into an integrated, cohesive unit. “It’s an open source language, available at www.prova.ws, and about 20 groups are using it around the world right now. We made it open source because you need to develop a community to keep a programming language alive,” says Dr Schroeder.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Properties of new materials for microchips
… can now be measured well. Reseachers of Delft University of Technology demonstrated measuring performance properties of ultrathin silicon membranes. Making ever smaller and more powerful chips requires new ultrathin…

Floating solar’s potential
… to support sustainable development by addressing climate, water, and energy goals holistically. A new study published this week in Nature Energy raises the potential for floating solar photovoltaics (FPV)…

Skyrmions move at record speeds
… a step towards the computing of the future. An international research team led by scientists from the CNRS1 has discovered that the magnetic nanobubbles2 known as skyrmions can be…





















