Penn study finds direct role for glial cells in brain cross-talk
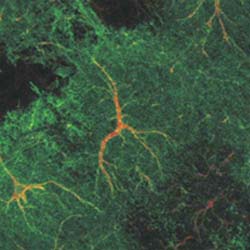
Astrocytes, a non-neuronal cell of the brain, are responsible for coordinating neuronal networks. Courtesy of Olivier Pascual and Philip Haydon, University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine, Department of Neuroscience
Findings may help elucidate mechanisms of wake-sleep transitions and epileptic seizures
Researchers at the University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine have demonstrated that star-shaped glial cells in the brain called astrocytes are directly involved in regulating communication between neurons. A central finding of the study is that astrocytes modulate the level of a signaling molecule called adenosine, which is thought to be important in controlling wake-to-sleep transitions and epileptic seizures.
“This finding may cause neuroscientists to radically alter their view of the role of astrocytes as merely supportive to one of actively communicating with and instructing neurons,” states senior author Philip G. Haydon, PhD, Professor of Neuroscience. “Astrocytes are not just the ’kitchen cells’ of the brain, providing nutritional support, but instead also help the neurons talk to each other.” Haydon and colleagues published their results in last week’s issue of Science.
The central nervous system, which includes the brain and spinal cord, is composed of specialized cells called neurons that send out and receive chemical signals called neurotransmitters across a space called the synapse. This process results in transmission of a nerve impulse. Historically, the glial cell or astrocyte was considered to be a support cell and to play no active role in regulating nerve impulse transmission. However, recent research by Haydon and other investigators has indicated that glial cells do produce chemical transmitters called gliotransmitters and that these chemical signals are recognized by the neurons. The studies that have shown capability were conducted on isolated nerve cells or on slices of brain tissue.
In this most recent study, the researchers made genetic manipulations to glial cells in live mice, thus directly demonstrating how astrocytes function in the brain. The mice were engineered to produce a protein called SNARE in their astrocytes. When the SNARE protein was produced, the amount of adenosine decreased.
When adenosine accumulated, nerve impulses were suppressed and could not be transmitted across the synapse. This helps explain why high adenosine levels can suppress epileptic seizures.
In contrast, low levels of adenosine increased the transmission of nerve impulses. The modulation of neuronal activity through the regulation of the level of adenosine in the synapse may explain the nature of wake-to-sleep transitions during periods of drowsiness.
“The next step is to study the behavior of these mice during manipulation of adenosine levels in the brain,” says Haydon.
The study was a collaboration between Haydon and Stephen Moss at Penn and Ken McCarthy, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill. The lead author was Olivier Pascual, a post-doctoral fellow in Penn’s Department of Neuroscience. Co-authors are Kristi Casper, Cathryn Kubera, Jing Zhang, Raquel Revilla-Sanchez, Jai-Yoon Sul and HajimeTakano.
This study was funded by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke and the National Institute of Mental Health. This release and related images can also be found at: www.uphs.upenn.edu/news
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.uphs.upenn.eduAll latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Properties of new materials for microchips
… can now be measured well. Reseachers of Delft University of Technology demonstrated measuring performance properties of ultrathin silicon membranes. Making ever smaller and more powerful chips requires new ultrathin…

Floating solar’s potential
… to support sustainable development by addressing climate, water, and energy goals holistically. A new study published this week in Nature Energy raises the potential for floating solar photovoltaics (FPV)…

Skyrmions move at record speeds
… a step towards the computing of the future. An international research team led by scientists from the CNRS1 has discovered that the magnetic nanobubbles2 known as skyrmions can be…





















