Nerve cells’ power plants caught in a traffic jam
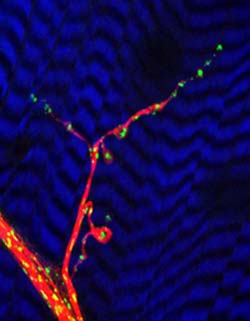
This image shows a neuromuscular junction, where a nerve cell connects to a muscle cell and delivers a signal to the muscle. The blue-and-black striped background is the muscle cell and the green dots are the neuron’s power plants, or mitochondria. The mitochondria move within the nerve cell along the pathways called microtubules, shown here in red. Photo credit: (c) 2005 Greg Macleod & Konrad Zinsmaier.
Nerve cells need lots of energy to work properly, and the energy needs to be delivered to the right place at the right time. By inducing a mutation in fruit flies, researchers have figured out that a particular gene governs the movement of cells’ energy-producing units, called mitochondria.
Rather than moving to the ends of the cells, or synapses, where cell-to-cell communication takes place, mitochondria in mutant fruit flies just piled up in the center of the cell. Even so, the mutant cells could still transmit signals, although not as well.
The findings are surprising because scientists had thought any disruption in normal mitochondrial behavior would be lethal in the embryo stage. Instead, the mutant fruit fly larvae survive for five days, although they don’t live to adulthood.
“Everyone believed that mitochondria are essential at synapses — and this is wrong,” said Konrad E. Zinsmaier, the University of Arizona associate professor of neuroscience who led the research team. “The mutation allows us to study what mitochondria are really good for.” The finding provides scientists with additional insight into how nerve cells work and provides a basis for understanding how such dysfunctions cause neurodegenerative diseases.
The researchers will publish their findings in the August 4 issue of the journal Neuron. A complete list of authors and their affiliations can be found at the end of this release.
Little is known about what causes mitochondria to become dysfunctional and how they contribute to neurological disorders. To learn more about what could go wrong with the energy units, Zinsmaier and his colleagues induced a mutation in the fruit fly mitochondrial protein, dMiro. dMiro stands for Drosophila mitochondrial Rho-like GTPase.
Molecular motors shuttle mitochondria within cells along cellular highways called microtubules. Normally, the mitochondria travel the length of the neuron until they reach the synapse. The mutation in the dMiro protein disabled the motor, disrupting the normal pattern of mitochondrial distribution.
The nerves’ synapses are where one nerve cell connects and communicates with other cells. For example, muscle cells contract when they receive the proper signals from nerve cells. Abnormal mitochondrial distribution within a neuron alters its ability to signal properly to adjoining muscle or nerve cells.
Instead of cruising smoothly along the microtubules, the mitochondria in mutant cells become caught in a traffic jam at the entrance ramp, located in the cell’s center.
Even though the synapses of the mutants are entirely devoid of mitochondria, the neuronal function remained intact at low levels of stimulation. But at high levels of stimulation, the mutated nerve cells failed.
Zinsmaier is now questioning the purpose of the mitochondria at the synapse. “How important are mitochondria?” he said. “We were surprised at how long the system could survive without them.” Zinsmaier explained that there may be a compensatory mechanism in place that is able to deal with minor mitochondrial dysfunction within the nerve.
Besides providing energy, mitochondria carry out other tasks important for cell survival. One important mitochondrial task is taking up excess calcium. Calcium is the main ingredient for proper neuron function. Too much calcium can lead to cell death. Zinsmaier hypothesizes that there could be a specialized communication system established within neurons involving another cell component that cooperates with mitochondria to properly store calcium.
While he has begun to piece together several theories, Zinsmaier explained that it remains unclear exactly how the compensation occurs. “The real surprise is that there are mechanisms in place that can manage the system somehow,” he said. “We didn’t know about them.”
The findings made by Zinsmaier and his colleagues have significant implications for neurobiologists, who may now begin looking more closely at defects in mitochondrial transport. Alterations in this process may help explain how and why human neurological diseases, such as muscular dystrophy and spastic paraplegia, develop.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.arizona.eduAll latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Silicon Carbide Innovation Alliance to drive industrial-scale semiconductor work
Known for its ability to withstand extreme environments and high voltages, silicon carbide (SiC) is a semiconducting material made up of silicon and carbon atoms arranged into crystals that is…

New SPECT/CT technique shows impressive biomarker identification
…offers increased access for prostate cancer patients. A novel SPECT/CT acquisition method can accurately detect radiopharmaceutical biodistribution in a convenient manner for prostate cancer patients, opening the door for more…

How 3D printers can give robots a soft touch
Soft skin coverings and touch sensors have emerged as a promising feature for robots that are both safer and more intuitive for human interaction, but they are expensive and difficult…





















