Co-operation between figs, wasps and parasites proves three is not always a crowd!

However, the long-term relationship between them can be threatened by individuals who take too much advantage of the relationship in the short-term for their own benefit. This new research suggests that the stable mutualism between tropical figs and pollinator wasps, which is about 100 million years old, may be maintained partly by parasitic wasps. This is contrary to the commonly held belief that parasites always have a negative effect.
The co-operative relationship between tropical figs and specialised pollinator wasps is such that the wasps pollinate the trees, and the trees provide resources for developing wasp offspring. The female wasp enters a fig fruit, and then pollinates the tiny flowers within the fruit. The tree’s seeds develop in parts of the flowers known as ovules, and the pollinator lays her eggs into some of these ovules. Importantly, ovules which contain developing seeds need to be free of wasp offspring because they eat the seeds. Therefore, each egg laid costs the tree one seed and in return, the female wasp’s offspring are responsible for dispersing the tree’s pollen once they leave the fig fruit. Trees need to produce both wasps and seeds for the mutualism to persist, but natural selection should favour wasps which exploit the maximum number of fig ovules in the short-term. This results in a conflict of interest between wasp and tree.
The fig fruits contain hundreds of ovules that can be grouped into ones which are situated closer to the centre of the fruit, known as inner ovules, and others which are further away from the centre of the fruit, known as outer ovules. Most pollinator wasp eggs are found in the inner ovules, whereas most fig seeds develop in the outer ovules. The female pollinator wasps avoid laying eggs in the outer ovules and this helps to keep the relationship between wasp and fig stable. This new research has found out that they do this because pollinator offspring developing in the outer ovules are at high risk of attack by parasitic wasps. These parasites lay their eggs directly into ovules from outside the fruit and will kill pollinator offspring. The risk from parasitic wasps is greatly reduced towards the centre of the fruit, which is likely to play a part in encouraging pollinators to avoid laying eggs in the outer ovules. It also reduces the total numbers of eggs which the wasps lay.
Professor James Cook, from the University’s School of Biological Sciences said “Inner ovules can provide an ‘enemy-free-space’ for pollinator wasps to lay their eggs in. Our results suggest that this favours pollinators that lay their eggs in the inner ovules and leave the outer ovules free for fig seeds to develop in. Because a wasp and a seed cannot develop in the same ovule, this is vital to ensuring that fig seed production is safeguarded. Parasitic wasps are generally thought to have negative effects on the relationship between figs and their pollinators, but our results show that in fact they may help to keep a mutualistic relationship stable in the natural world.”
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.reading.ac.ukAll latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Wildfire danger to increase due to climate change
WSL Institute for Snow and Avalanche Research (SLF) researchers expect an elevated wildfire danger in the Alpine Foreland from 2040 onwards due to changing meteorological conditions. The danger currently remains…
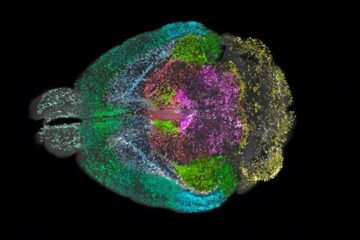
Advanced Brain Science Without Coding Expertise
Researchers at Helmholtz Munich and the LMU University Hospital Munich introduce DELiVR, offering a new AI-based approach to the complex task of brain cell mapping. The deep learning tool democratizes…
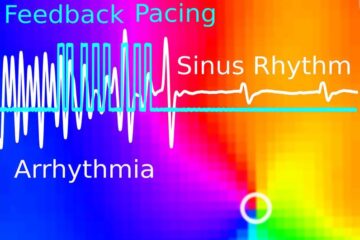
Gentle defibrillation for the heart
Using light pulses as a model for electrical defibrillation, Göttingen scientists developed a method to assess and modulate the heart function. The research team from the Max Planck Institute for…





















