In vivo visualization of alternative splicing

Dr. Hidehito Kuroyanagi and colleagues at the Tokyo Medical and Dental University engineered a transgenic alternative splicing reporter system to monitor the developmentally regulated switching of let-2 alternative splicing in live C. elegans worms.
The splicing of let-2 changes during the lifetime of the worm: Embryos and early larvae express exon 9, while adult worms express exon 10. By linking exons 9 and 10 with differently colored fluorescent proteins (green and red, respectively).
Drs. Kuroyanagi & Hagiwara's team was able to visually monitor let-2 splicing patterns during the life of an individual worm.
“The reporter system enables experimental analysis of regulation mechanisms underlying the developmental or cell-type-specific profiles of alternative splicing in living organisms.
We are coming to realize that the molecular mechanisms of alternative splicing are highly conserved throughout metazoan evolution,” explains Dr. Kuroyanagi.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.cshl.eduAll latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Wildfire danger to increase due to climate change
WSL Institute for Snow and Avalanche Research (SLF) researchers expect an elevated wildfire danger in the Alpine Foreland from 2040 onwards due to changing meteorological conditions. The danger currently remains…
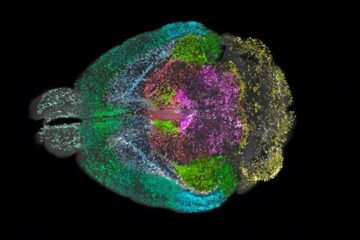
Advanced Brain Science Without Coding Expertise
Researchers at Helmholtz Munich and the LMU University Hospital Munich introduce DELiVR, offering a new AI-based approach to the complex task of brain cell mapping. The deep learning tool democratizes…
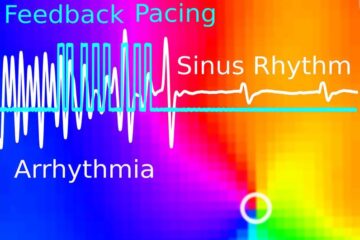
Gentle defibrillation for the heart
Using light pulses as a model for electrical defibrillation, Göttingen scientists developed a method to assess and modulate the heart function. The research team from the Max Planck Institute for…





















