Quality Control in Cells
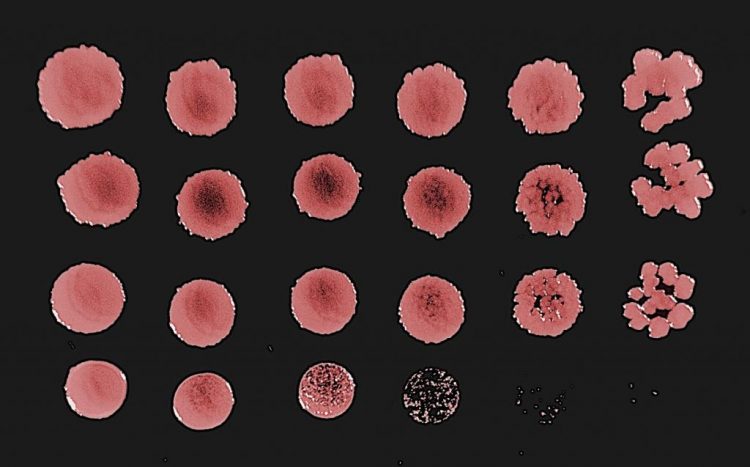
Das Bild zeigt eine Falschfarben-Darstellung von Kolonien von Bacillus subtilis-Bakterien, die entweder genetisch unverändert sind oder einzelne oder kombinierte Mutationen tragen, die ihre Qualitätskontrollprozesse für Proteine inaktivieren (darunter auch RQC). Dieser Wachstumstest zeigt in jeder Zeile von links nach rechts, dass die Bakterienzellen mit den kombinierten Mutationen unter bestimmten Bedingungen immer schlechter wachsen. | © C. Joazeiro
A protective protein that can detect newly-made incomplete and hence potentially toxic protein chains in higher cells is found to have a relative in bacteria. There, the protein also plays a central role in quality control which ensures that defective proteins are degraded.
The functional mechanism of these evolutionarily related Rqc2 proteins thus acts as key quality control component and must therefore have already existed several billion years ago in the so-called last universal common ancestor.
Scientists at the Center for Molecular Biology of Heidelberg University (ZMBH) have reached this conclusion based on their experimental study of the function of the bacterial Rqc2 relative.
In cells, incomplete protein chains originate regularly due to problems during their synthesis. Such aberrant chains are potentially toxic to cells and must be eliminated.
In cells of eukaryotic organisms – such as fungi, plants and animals – a quality control process, known as Ribosome-associated Quality Control (RQC), leads to the disposal of those defective proteins.
A key component of RQC is the Rqc2 protein, which is responsible for sensing the aberrant protein chains, and for recruiting an enzyme that labels the defective protein for degradation. Interestingly, bacteria also have been known to possess proteins similar to the Rqc2 protein of higher organisms. Until now, however, these proteins were thought to have a different function in bacteria.
Using Bacillus subtilis bacteria, the research team at the ZMBH led by Prof. Dr Claudio Joazeiro has now been able to experimentally demonstrate that their Rqc2 protein is also able to recognise incompletely synthesised proteins.
However, unlike in higher cells, the Rqc2 protein in bacteria itself marks the aberrant chains; it appends them with a poly-alanine chain to trigger their elimination by the bacterial disposal system. The researchers also showed that this is an important protective mechanism against the cellular stress caused by defective protein production.
The Heidelberg research results demonstrate that the evolutionarily related Rqc2 proteins in bacteria and higher cells perform this quality control function in a similar manner. This led the scientists to conclude that this mechanism must have already existed several billion years ago in the so-called last universal common ancestor, and that this protective function is among the most elemental and essential processes of all cells.
In fact, Prof. Joazeiro had previously shown that a mutation preventing the process from functioning causes degeneration of neuronal cells in a similar manner to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), a devastating human disease.
Researchers from Berlin, Marburg, and the USA were also involved in the research, which was supported by the German Research Foundation, among others within the framework of the Collaborative Research Centre “Cellular Surveillance and Damage Response” (CRC 1036). The results of their research were published in “Cell”.
Contact:
Heidelberg University
Communications and Marketing
Press Office, phone +49 6221 54-2311
presse@rektorat.uni-heidelberg.de
Prof. Dr Claudio Joazeiro
Center for Molecular Biology of Heidelberg University
Phone +49 6221 54-6858
c.joazeiro@zmbh.uni-heidelberg.de
I. Lytvynenko, H. Paternoga, A. Thrun, A. Balke, T.A. Müller, C.H. Chiang, K. Nagler, G. Tsaprailis, S. Anders, I. Bischofs, J.A. Maupin-Furlow, C.M.T. Spahn, C. A.P. Joazeiro: Alanine Tails Signal Proteolysis in Bacterial Ribosome-Associated Quality Control, Cell 178, 76–90, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2019.05.002
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.uni-heidelberg.deAll latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Properties of new materials for microchips
… can now be measured well. Reseachers of Delft University of Technology demonstrated measuring performance properties of ultrathin silicon membranes. Making ever smaller and more powerful chips requires new ultrathin…

Floating solar’s potential
… to support sustainable development by addressing climate, water, and energy goals holistically. A new study published this week in Nature Energy raises the potential for floating solar photovoltaics (FPV)…

Skyrmions move at record speeds
… a step towards the computing of the future. An international research team led by scientists from the CNRS1 has discovered that the magnetic nanobubbles2 known as skyrmions can be…





















