Protein anchors help keep embryonic development 'just right'
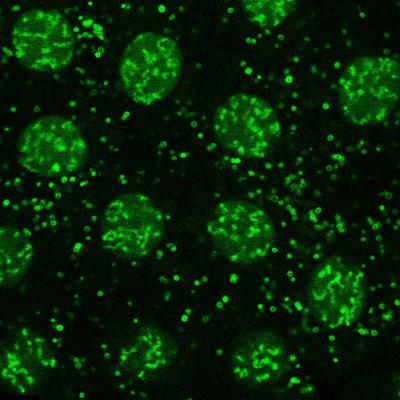
Histones (shown in green) in fruit fly embryos. They are stored on lipid droplets (small dots/rings) and -- when needed -- travel to nuclei (large spheres) to package DNA into chromosomes. Credit: Photo by Zhihuan Li/University of Rochester.
It's been known that specific proteins, called histones, must exist within a certain range—if there are too few, a fruit fly's DNA is damaged; if there are too many, the cell dies.
Now research out of the University of Rochester shows that different types of histone proteins also need to exist in specific proportions. The work further shows that cellular storage facilities keep over-produced histones in reserve until they are needed.
Associate Professor of Biology Michael Welte has discovered that the histone balance is regulated by those storage facilities, called lipid droplets—which are best known as fat depots.
The findings were published today in the journal Current Biology.
Welte had previously discovered that another protein—called Jabba—anchored histones onto lipid droplets. In his latest research, he found that excess histones migrate outside the nucleus to the droplets, where they are temporarily held until needed to create new chromosomes.
“People have observed histone proteins on lipid droplets in multiple organisms, including mammals,” said Welte. “The results of this research project may very well help us understand the role of histones and lipid droplets in humans.”
Welte found that by deleting the Jabba anchors from the cell, one particular type of histone increased in proportion in the nucleus, since they had no way to be held in reserve away from the cell nuclei. That made the embryo more sensitive to environmental stresses like higher temperature, leading to defects during cell division and reduced viability.
Just as it is in humans, the embryonic stage is a crucial time for the fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster). Starting from a single cell, it has to rapidly multiply in cell number and develop into a larva while coping with stresses from the environment. The embryo does all of that by activating a myriad of genetic on-off switches, a process that involves unwrapping and rewrapping various regions of DNA.
Histones are important to the process because they act as spools that DNA molecules wrap around to form chromosomes, making it possible for the DNA to do its work in the first place. Welte discovered that if the different histones are not in the correct proportion, the embryo has trouble developing correctly and may even die.
Achieving the correct proportion of histones is not something that happens automatically in the fruit fly embryo, as Welte found in his research. Instead, when a certain histone type is made in excess, it is redirected to the lipid-droplet holding sites outside the nucleus where it is kept until needed.
Welte and his team will try next to identify which parts of the Jabba protein actually bind with the histone. Once that's determined, scientists may have the ability to manipulate the histone storage process.
“Since histones and lipid droplets are found in humans, I very much expect that there will be a similar storage process,” said Welte. “If that is the case, our findings could one day help treat or prevent diseases linked to chromosome malfunction. What I find most fascinating is that our research uncovered this intimate link between cellular fat depots and the nucleus, a connection that just a few years ago nobody would have dreamt of. “
The research team included Zhihuan Li, Matthew Johnson, Zhonghe Ke and Lili Chen. The research was supported by a grant from the National Institutes of Health.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Properties of new materials for microchips
… can now be measured well. Reseachers of Delft University of Technology demonstrated measuring performance properties of ultrathin silicon membranes. Making ever smaller and more powerful chips requires new ultrathin…

Floating solar’s potential
… to support sustainable development by addressing climate, water, and energy goals holistically. A new study published this week in Nature Energy raises the potential for floating solar photovoltaics (FPV)…

Skyrmions move at record speeds
… a step towards the computing of the future. An international research team led by scientists from the CNRS1 has discovered that the magnetic nanobubbles2 known as skyrmions can be…





















