pH Sensor for Cell Organelles
<br>
Acidity (pH) and its changes play an important role in many physiological processes, including protein folding, and can act as indicators of cancer. In the journal Angewandte Chemie, American researchers have now introduced an unconventional pH sensor that makes it possible to monitor changes in pH values in living cells over longer periods of time, with previously unobtainable spatial resolution. This is possible through the combination of fluorescent nanocrystals with mobile molecular “arms” that can fold or unfold depending on the pH of their environment.
Endosomes, cell organelles that play a role in transport within cells, experience a considerable drop in their pH value as they mature. This was observed by the team working with Moungi G. Bawendi at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in Cambridge (USA) by using a new nanoscopic pH sensor and a fluorescence microscope.
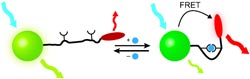
The secret to their success lies in the unconventional design of their sensor: A mobile molecular “arm” connects a green fluorescent nanocrystal to a red fluorescent dye. The nanocrystals are particles of semiconductor materials that easily transfer the light energy they absorb to fluorescent dyes through a radiation-free mechanism (fluorescence resonance energy transfer, or FRET). This causes the dye to fluoresce—as long as both of the FRET partners are close enough to each other.
The distance between the nanocrystal and the dye is controlled by folding and unfolding of the molecular arm on the nano pH sensor—and this motion is pH-dependent. The arm consists of one piece of double-stranded and one piece of single-stranded DNA. As the concentration of H+ ions increases, so does the tendency to form a “triple strand”, in which the single strand fits into the groove of the double strand, causing the arm to fold. This “arm movement” takes place in the physiologically important range around pH 7 and is very sensitive to the slightest change.
At higher pH values, the arm is stretched out and the FRET partners are too far away from each other for energy transfer to occur. The nanocrystal emits green fluorescence and the dye does not fluoresce. As the pH gets lower, the arm folds enough to allow FRET energy transfer. The green fluorescence of the nanocrystal decreases and the dye begins to glow red. Because this technique measures the ratio of green to red fluorescence instead of an absolute value, variations in intensity make no difference. The sensor thus has an internal reference.
In this type of sensor, the actual “pH tester” and the optical signaling device are two separate components. By replacing the pH tester with a molecular arm that responds to a different analyte it should be possible to use the same principle and the same optical signaling device to build sensors for other target molecules.
Nanocrystal fluorophores have caused much excitement in several fields because of their attractive optical properties. Nanocrystals offer superior properties compared to traditional molecular fluorophores, in particular in biology, where they can help reveal the inner workings of the cell. However, converting these new nanomaterials into fluorescent sensors has proven difficult. The concept of harnessing a molecular conformational change to create a sensor is new for nanocrystal sensors and could prove a general solution to the problem of making sensors from nanocrystals.
Author: Moungi G. Bawendi, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge (USA), http://nanocluster.mit.edu/people.php
Title: Conformational Control of Energy Transfer: A Mechanism for Biocompatible Nanocrystal-Based Sensors
Angewandte Chemie International Edition, Permalink to the article: http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/anie.201207181
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Silicon Carbide Innovation Alliance to drive industrial-scale semiconductor work
Known for its ability to withstand extreme environments and high voltages, silicon carbide (SiC) is a semiconducting material made up of silicon and carbon atoms arranged into crystals that is…

New SPECT/CT technique shows impressive biomarker identification
…offers increased access for prostate cancer patients. A novel SPECT/CT acquisition method can accurately detect radiopharmaceutical biodistribution in a convenient manner for prostate cancer patients, opening the door for more…

How 3D printers can give robots a soft touch
Soft skin coverings and touch sensors have emerged as a promising feature for robots that are both safer and more intuitive for human interaction, but they are expensive and difficult…





















