The pathway into the cell
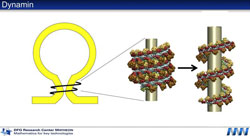
In the case of dynamin, the precise mechanism of action can be visualised in individual steps<br>Noe<br>
“Imagine an inflated balloon attached to a pump, but much, much smaller. By pinching off the neck of the balloon with a noose, it is detached from the pump and is able to move about freely.” The description is an approximation of one of the molecular processes looked at by mathematician Dr. Frank Noe as part of MATHEON’S ‘A19, Modelling and Optimisation of Functional Molecules’ project. Specifically, the molecular structure and mechanism of dynamin.
Dynamin is a protein and the ‘noose’ which detaches the balloon from the pump. The vesicle (the scientific name for the balloon) has to be detached to allow it to perform its role as a vesicle for transporting messenger substances and nutrients into the cell. Substances which need to be transported into the cell first accumulate in a vesicle formed by invagination from the surface of the cell. The dynamin molecule then attaches to the neck of the vesicle and forms a spiral around it. It then severs the neck of the vesicle. The vesicle is now free to transport nutrients into the cell.
Whilst scientists have long known about the process, the molecular details of how dynamin works were until now unknown. A group of researchers at the Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine (MDC) in Berlin has now managed to obtain snapshots of the detailed molecular structure and, with the help of mathematical research carried out by Frank Noe and his team at MATHEON, been able to breathe life into these static structures.
“Without mathematical methods, it would not have been possible to simulate the processes which occur when the neck of the vesicle is severed,” explains the mathematician.
Simulating this molecular process is extremely difficult. “A simulation encompasses 250,000 particles and each iteration of the calculation takes around 1 second, even on a mainframe. To directly simulate this process, we would have to perform millions of iterations. That would take decades – scission within the cell takes just milliseconds.” With the help of mathematical methods developed at MATHEON, it was possible to divide the scission process up into many smaller, more manageable simulations.
In the case of dynamin, this allowed the precise mechanism of action to be visualised in individual steps. It turns out that the molecule operates via a specific pathway. “We were able to identify three primary states of the molecule,” explains the mathematician, describing the process as follows, “Initially, dynamin molecules attach to the neck of the vesicle individually, before linking up to form between one and a half and two tight turns around the neck of the vesicle. This structure then expands like a spring and rotates in on itself. The result is that the semi-fluid material making up the neck of the vesicle is more or less ripped apart. “
Understanding this process is important for medical science, as it represents a point of attack for fighting poisons and disease. “Many neurotoxins, for example, act at this point, thereby blocking nerve function,” explains Frank Noe. Degenerative neurological diseases such as Parkinson’s also affect the uptake of vesicles by nerve cells. “If we can obtain a better understanding of the mechanism of dynamin, we may be able to find new approaches to early diagnosis or treatments,” says Dr. Noe.
Collaboration between doctors, structural biologists and mathematicians in this area is set to continue. “The mathematical research being carried out within the MATHEON project will continue to make an important contribution to producing further useful insights,” explains Frank Noe.
The study has been published in the journal ‘Nature’, issue 477, page 556. Further information on the study can be found at
http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v477/n7366/full/nature10369.html
and
www.biocomputing-berlin.de/biocomputing/en/projects/matheon_project_
a19_modelling_and_optimization_of_functional_molecules
Frank Noe will also be happy to provide you with further information and can be contacted by telephone on 030 838 75354 or by email at noe@math.fu-berlin.de
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

High-energy-density aqueous battery based on halogen multi-electron transfer
Traditional non-aqueous lithium-ion batteries have a high energy density, but their safety is compromised due to the flammable organic electrolytes they utilize. Aqueous batteries use water as the solvent for…

First-ever combined heart pump and pig kidney transplant
…gives new hope to patient with terminal illness. Surgeons at NYU Langone Health performed the first-ever combined mechanical heart pump and gene-edited pig kidney transplant surgery in a 54-year-old woman…

Biophysics: Testing how well biomarkers work
LMU researchers have developed a method to determine how reliably target proteins can be labeled using super-resolution fluorescence microscopy. Modern microscopy techniques make it possible to examine the inner workings…





















