New risk factors for anxiety disorders
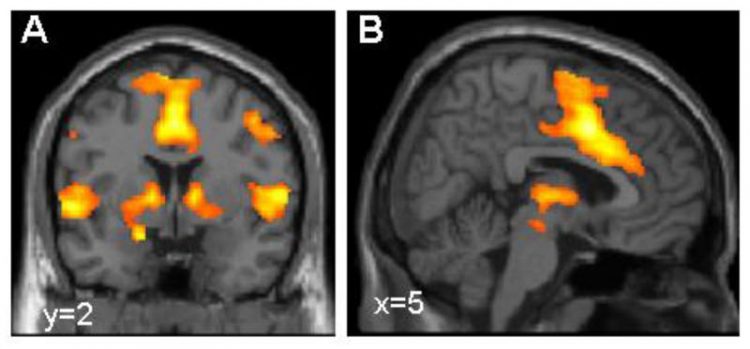
Activation of the brain's fear network, visualized using functional magnetic resonance imaging (picture: Dr. Tina Lonsdorf, Systems Neuroscience UKE Hamburg)
Mental, social and inherited factors all play a role in anxiety disorders. In the journal “Molecular Psychiatry”, a research team from Julius-Maximilians-Universität Würzburg (JMU) in Bavaria, Germany, describes a hitherto unknown genetic pathway for developing such diseases:
They pinpointed at least four variants of the GLRB gene (glycine receptor B) as risk factors for anxiety and panic disorders. More than 5000 voluntary participants and 500 patients afflicted by panic disorder took part in the study that delivered these results.
In Germany, around 15 percent of adults suffer from anxiety and panic disorders. Some people may have an extreme fear of spiders or other objects while others have breathing difficulties and accelerated heart beat in small rooms or large gatherings of people.
With some afflicted persons, the anxiety attacks occur for no apparent cause. Many patients suffer from the detrimental impacts on their everyday lives – they often have problems at work and withdraw from social contacts.
How are fear and anxiety triggered? How do anxiety disorders arise and evolve?
Scientists from Münster, Hamburg and Würzburg have looked into these questions within the scope of Collaborative Research Center (CRC) TR 58 funded by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft. Their goal is to develop new therapies that are better tailored to the individual patients. Anxiety disorders can be treated with drugs and behaviour therapy for instance.
Gene triggers hyperekplexia
The discovery that different variants of the GLRB gene are associated with anxiety disorders might also contribute to the development of improved therapies. The gene had been known to the researchers for some time, albeit only in connection with a different disease:
“Some mutations of the gene cause a rare neurological disorder called hyperekplexia,” explains Professor Jürgen Deckert, member of the CRC and Director of the Department of Psychiatry at the JMU University Hospital. The patients are permanently hypertonic and show pronounced startle responses, which may even cause sufferers to fall involuntarily. Similar to persons suffering from anxiety disorders, these patients develop behaviour to avoid potentially frightening situations.
The “fear network” in the brain is activated
But the GLRB gene variants that have recently been associated with anxiety and panic disorders for the first time are different from the ones described above. They occur more frequently and presumably entail less severe consequences. But they, too, trigger overshooting startle responses, and as a result may excessively activate the brain's “fear network”. High-resolution images of the brain activities of study participants provided the clues for the Würzburg scientists.
“The results point to a hitherto unknown pathway of developing an anxiety disorder,” Deckert says. He believes that further investigations are now necessary to determine whether these findings can be harnessed to develop new or individual therapies. For example, it is conceivable to bring the “fear network” that is misregulated by the GLRB gene back on track by administering drugs.
CRC collaborates with panic network
The members of the Collaborative Research Center “Fear, Anxiety and Anxiety Disorders” obtained these results in cooperation with researchers from the “PanikNetz” panic network. The Würzburg team is part of the network that is funded by the Federal Ministry for Education and Research.
“GLRB allelic variation associated with agoraphobic cognitions, increased startle response and fear network activation: a potential neurogenetic pathway to panic disorder”, Molecular Psychiatry, published online on 7 February 2017, DOI: 10.1038/mp.2017.2
Contact
Prof. Dr. Jürgen Deckert, Chair of Psychiatry and Psychotherapy of the University of Würzburg, T + 49 931 201-77000, deckert_j@ukw.de
https://campus.uni-muenster.de/sfbtrr58/the-project/ Collaborative Research Center “Fear, Anxiety and Anxiety Disorders”
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.uni-wuerzburg.deAll latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Superradiant atoms could push the boundaries of how precisely time can be measured
Superradiant atoms can help us measure time more precisely than ever. In a new study, researchers from the University of Copenhagen present a new method for measuring the time interval,…

Ion thermoelectric conversion devices for near room temperature
The electrode sheet of the thermoelectric device consists of ionic hydrogel, which is sandwiched between the electrodes to form, and the Prussian blue on the electrode undergoes a redox reaction…

Zap Energy achieves 37-million-degree temperatures in a compact device
New publication reports record electron temperatures for a small-scale, sheared-flow-stabilized Z-pinch fusion device. In the nine decades since humans first produced fusion reactions, only a few fusion technologies have demonstrated…





















