New metabolism discovered in bacteria
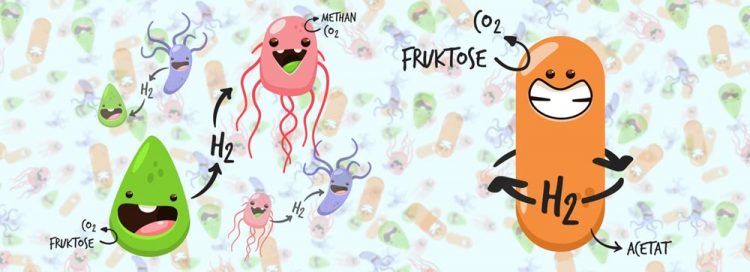
While acetic acid creating bacteria and methanogens are dependent on the transfer of hydrogen in anoxic biotopes, Acetobacterium woodii recycles hydrogen within its cell. Illustration: Sarah Ciurus, Goethe University Frankfurt, Germany
They make sauerkraut sour, turn milk into yogurt and cheese, and give rye bread its intensive flavour: bacteria that ferment nutrients instead of using oxygen to extract their energy. Acetobacterium woodii (short: A. woodii) is one of these anaerobic living microbes.
Cheese and bread are not its line of business – it lives far from oxygen in the sediments on the floor of the ocean, and can also be found in sewage treatment plants and the intestines of termites.
These biotopes are teeming with microbes that use the organic substances to their advantage in different ways. A number of bacteria ferment sugars, fatty acids and alcohols to acetic acid, also creating hydrogen (H2) in the process. In higher concentration, however, hydrogen inhibits the fermentation – too much hydrogen stops the fermentation reaction.
For this reason, fermenting bacteria live together with microbes that depend on precisely this hydrogen, methanogens, for example, that create methane from hydrogen and carbon dioxide and thus gain energy. Both partners profit from this association – and are simultaneously so dependent on each other that neither one can survive without the other.
A. woodii masters both disciplines of the anaerobic “hydrogen association”: it can ferment organic substances into acetic acid, and can also form acetic acid from carbon dioxide and hydrogen.
In doing so, A. woodii recycles the important hydrogen within its own cell, as has now been discovered by the microbiologists in Professor Volker Müller’s team at the Institute for Molecular Biosciences at Goethe University Frankfurt, Germany.
In the laboratory, the Frankfurt scientists turned off the gene for the enzyme that creates hydrogen in A. woodii, which is called hydrogenase. The result: the bacterium was only able to grow, for example in a medium with fructose, if hydrogen was added externally. Different additional tests confirmed that both paths for creating acetic acid are connected to hydrogen that does not leave the cell.
“Though the ‘hydrogen recycling’ we discovered, A. woodii possesses a maximum of metabolic flexibility,” says the Frankfurt experimenter Dr Anja Wiechmann. “In one cycle, it can both create and use hydrogen itself, or utilise hydrogen from external sources. This makes it capable of living both from organic as well as solely from inorganic substances.”
Professor Volker Müller explains: “Our findings have implications far beyond the study of Acetobacterium woodii. There have already been speculations that many ancient life forms possess the kind of metabolism that we have described in A. woodii. This is assumed, for example for the Asgard archaea that were just discovered a few years ago on the seabed off of California. Our investigations provide the first evidence that these paths of metabolism actually exist.”
Prof. Volker Müller
Department for Molecular Microbiology and Bioenergetics
Institute for Molecular Biosciences
Goethe University Frankfurt, Germany
Phone.: +49 69 798-29507
VMueller@bio.uni-frankfurt.de
Publication: Anja Wiechmann, Sarah Ciurus, Florian Oswald, Vinca Seiler, Volker Müller (2020). It does not always take two to Tango: „Syntrophy“ via hydrogen cycling in one bacterial cell. ISME Journal, (https://doi.org/10.1038/s41396-020-0627-1)
http://www.uni-frankfurt.de/86948227 Image to be downloaded. Caption: While acetic acid creating bacteria and methanogens are dependent on the transfer of hydrogen in anoxic biotopes, Acetobacterium woodii recycles hydrogen within its cell (Illustration: Sarah Ciurus, Goethe University Frankfurt, Germany).
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Superradiant atoms could push the boundaries of how precisely time can be measured
Superradiant atoms can help us measure time more precisely than ever. In a new study, researchers from the University of Copenhagen present a new method for measuring the time interval,…

Ion thermoelectric conversion devices for near room temperature
The electrode sheet of the thermoelectric device consists of ionic hydrogel, which is sandwiched between the electrodes to form, and the Prussian blue on the electrode undergoes a redox reaction…

Zap Energy achieves 37-million-degree temperatures in a compact device
New publication reports record electron temperatures for a small-scale, sheared-flow-stabilized Z-pinch fusion device. In the nine decades since humans first produced fusion reactions, only a few fusion technologies have demonstrated…





















