Nerves as never before
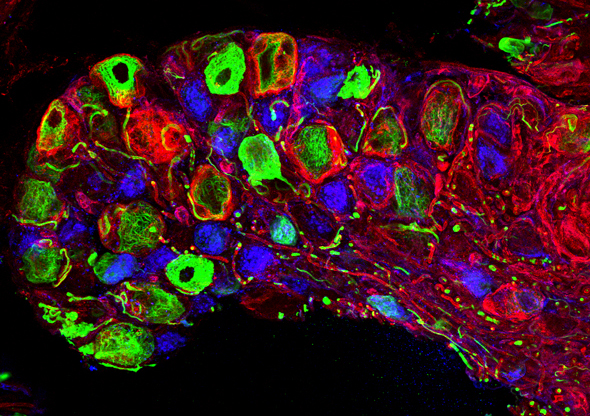
Image credit: EMBL/L.Castaldi
The riot of colour before your eyes provides a glimpse at another sense: touch.
When something brushes a mouse’s skin, or the temperature around it changes, this bundle of nerves relays that information from touch receptors on the skin to the spinal cord and ultimately the brain, where it can be processed and acted upon.
Neurons involved in sensing light touch are shown in green, and two different types of nerve cell involved in sensing pain are labelled red and blue.
The image was obtained through a novel technique developed by Paul Heppenstall’s lab at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Monterotondo, Italy, which enables researchers to explore tissues in mice in much greater detail than ever before.
Published online in Nature Methods on 8 December 2014. DOI: 10.1038/nmeth.3207.
Additional images and extended captions: www.embl.org/press/2014/141208_Monterotondo_picr .
For more information please visit: www.embl.org/press/2014/141208_Monterotondo .
***High resolution images available upon request.***
——————————
Policy regarding use
EMBL press and picture releases including photographs, graphics and videos are copyrighted by EMBL. They may be freely reprinted and distributed for non-commercial use via print, broadcast and electronic media, provided that proper attribution to authors, photographers and designers is made.
——————————
Sonia Furtado Neves
EMBL Press Officer & Deputy Head of Communications
Meyerhofstr. 1, 69117 Heidelberg, Germany
Tel.: +49 (0)6221 387 8263
Fax: +49 (0)6221 387 8525
sonia.furtado@embl.de
http://s.embl.org/press
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Properties of new materials for microchips
… can now be measured well. Reseachers of Delft University of Technology demonstrated measuring performance properties of ultrathin silicon membranes. Making ever smaller and more powerful chips requires new ultrathin…

Floating solar’s potential
… to support sustainable development by addressing climate, water, and energy goals holistically. A new study published this week in Nature Energy raises the potential for floating solar photovoltaics (FPV)…

Skyrmions move at record speeds
… a step towards the computing of the future. An international research team led by scientists from the CNRS1 has discovered that the magnetic nanobubbles2 known as skyrmions can be…





















