Nanotechnology reveals hidden depths of bacterial 'machines'
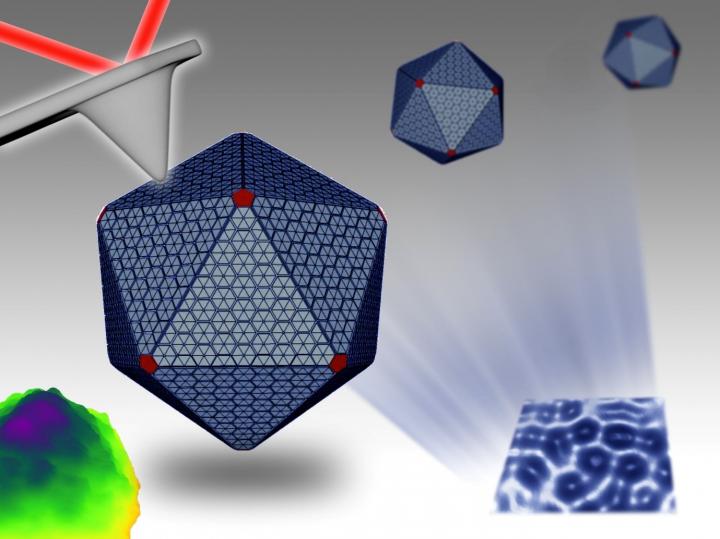
This is an illustration of a carboxysome. Credit Dr Luning Liu, University of Liverpool
Cyanobacteria are a phylum of bacteria that produce oxygen and energy during photosynthesis, similar to green plants. They are among the most abundant organisms in oceans and fresh water. Unique internal 'machines' in cyanobacteria, called carboxysomes, allow the organisms to convert carbon dioxide to sugar and provide impacts on global biomass production and our environment.
Carboxysomes are nanoscale polyhedral structures that are made of several types of proteins and enzymes. So far, little is known about how these 'machines' are constructed and maintain their organisation to perform carbon fixation activity.
Researchers from the University's Institute of Integrative Biology, led by Royal Society University Research Fellow Dr Luning Liu, examined in depth the native structure and mechanical stiffness of carboxysomes using advanced microscopes and biochemical approaches.
For the first time, the researchers were able to biochemically purify active carboxysomes from cyanobacteria and characterize their carbon fixation activity and protein composition. They then used electron microscopy and atomic force microscopy to visualise the morphology and internal protein organization of these bacterial machines.
Furthermore, the intrinsic mechanical properties of the three-dimensional structures were determined for the first time. Though structurally resembling polyhedral viruses, carboxysomes were revealed to be much softer and structurally flexible, which is correlated to their formation dynamics and regulation in bacteria.
Dr Liu, said: “It's exciting that we can make the first 'contact' with these nano-structures and understand how they are self-organised and shaped using state-of-the-art techniques available at the University. Our findings provide new clues about the relationship between the structure and functionality of native carboxysomes.”
The self-assembly and modularity features of carboxysomes make them interesting systems for nanoscientists, synthetic biologists and bioengineers, who hope to find ways to design new nanomaterials and nano-bioreactors.
“We're now just starting to understand how these bacterial machines are built and work in nature. Our long-term vision is to harness the knowledge to make further steps towards better design and engineering of bio-inspired machines,” added Dr Liu, “The knowledge and techniques can be extended to other biological machines.”
###
The project was done in collaboration with Professor Rob Beynon at the University's Centre for Proteome Research and the Centre for Cell Imaging and funded by the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC) and a Royal Society University Research Fellowship.
The paper 'Direct characterization of the native structure and mechanics of cyanobacterial carboxysomes' is published in the journal Nanoscale [DOI: 10.1039/C7NR02524F]
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Superradiant atoms could push the boundaries of how precisely time can be measured
Superradiant atoms can help us measure time more precisely than ever. In a new study, researchers from the University of Copenhagen present a new method for measuring the time interval,…

Ion thermoelectric conversion devices for near room temperature
The electrode sheet of the thermoelectric device consists of ionic hydrogel, which is sandwiched between the electrodes to form, and the Prussian blue on the electrode undergoes a redox reaction…

Zap Energy achieves 37-million-degree temperatures in a compact device
New publication reports record electron temperatures for a small-scale, sheared-flow-stabilized Z-pinch fusion device. In the nine decades since humans first produced fusion reactions, only a few fusion technologies have demonstrated…





















