Melanoma-promoting gene discovered
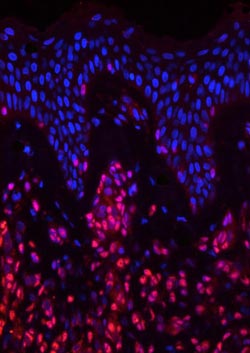
The stem-cell factor Sox10 (red) is active in the tumor tissue of melanoma patients and essential for the development and spread of cancer.<br>Olga Shakhova<br>
Despite intensive research, however, there is still no treatment. Researchers from the University of Zurich have now discovered a gene that plays a central role in black skin cancer. Suppressing this gene in mice inhibits the development of melanoma and its proliferation – a discovery that could pave the way for new forms of therapy.
Until recently, it was assumed that a tumor was composed of many equivalent cells that all multiply malignantly and can thus contribute towards tumor growth. According to a more recent hypothesis, however, a tumor might also consist of malignant cancer stem cells and other less aggressive tumor cells. Normally, stem cells are responsible for the formation of organs.
Cancer stem cells can divide in a very similar way and develop into other tumor cells to form the tumor. Efficient tumor therapy thus primarily needs to fight cancer stem cells. Consequently, a team of stem-cell researchers from the University of Zurich headed by Professor Sommer decided to find out whether mechanisms that are important for normal stem cells also play a role in cancer stem cells.
Regulating gene discovered in tumor
Melanoma cells are rogue skin-pigment cells formed by so-called neural crest stem cells during embryonic development. Professor Sommer’s group teamed up with dermatologists and pathologists to investigate whether cells with characteristics of these specific stem cells are present in human tumor tissue.
“This was indeed the case, as we were able to prove based on numerous biopsies performed on melanoma patients,” says Sommer. In particular, one gene that effectively controls the stem-cell program was highly active in all the tumor tissue studied. This gene, which is known as “Sox10”, is essential for cell division and the survival of stem cells.
Gene suppression inhibits cancer
The next step for the Zurich researchers was to test how Sox10 works in human melanoma cells. They determined that the gene also controls a stem-cell program in cancer cells and is necessary for cell division. In order to corroborate these findings in a living organism, the researchers ultimately used a mouse which carried similar genetic mutations to those found in human melanoma and thus developed black skin cancer spontaneously. Astonishingly, the suppression of Sox10 in this animal model completely inhibited the formation and spread of cancer.
“Our research demonstrates that a tumor could probably be treated by attacking its stem cells,” concludes Sommer. The results also illustrate that such studies can primarily be successful through the close collaboration and conscious use of synergies between basic researchers and clinicians.
Further reading:
Olga Shakhova, Daniel Zingg, Simon M. Schaefer, Lisette Hari, Gianluca Civenni, Jacqueline Blunschi, Stéphanie Claudinot, Michal Okoniewski, Friedrich Beermann, Daniela Mihic-Probst, Holger Moch, Michael Wegner, Reinhard Dummer, Yann Barrandon, Paolo Cinelli, and Lukas Sommer. Sox10 promotes the formation and maintenance of giant congenital naevi and melanoma. Nature Cell Biology. 8 July, 2012. Doi: 10.1038/ncb2535
Contact:
Professor Lukas Sommer
Institute of Anatomy
University of Zurich
Tel.: +41 44 635 53 50
Email: lukas.sommer@anatom.uzh.ch
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.uzh.chAll latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Superradiant atoms could push the boundaries of how precisely time can be measured
Superradiant atoms can help us measure time more precisely than ever. In a new study, researchers from the University of Copenhagen present a new method for measuring the time interval,…

Ion thermoelectric conversion devices for near room temperature
The electrode sheet of the thermoelectric device consists of ionic hydrogel, which is sandwiched between the electrodes to form, and the Prussian blue on the electrode undergoes a redox reaction…

Zap Energy achieves 37-million-degree temperatures in a compact device
New publication reports record electron temperatures for a small-scale, sheared-flow-stabilized Z-pinch fusion device. In the nine decades since humans first produced fusion reactions, only a few fusion technologies have demonstrated…





















