Like a zipper – How cells form new blood vessels
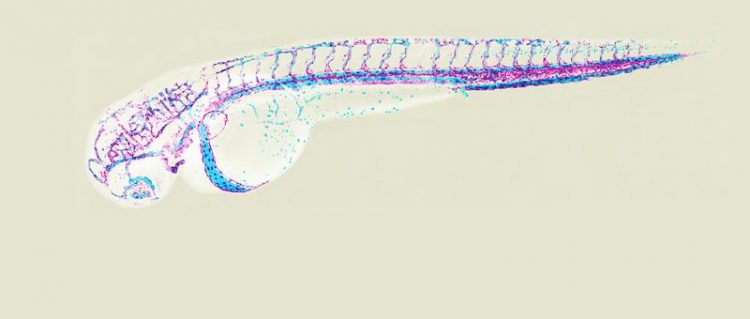
Vascular system of a two days old zebrafish embryo (magenta: endothelial cells, light blue: blood cells). Image: University of Basel, Biozentrum
The blood vessels form a widely ramified supply system that passes through our body from head to toe. They serve as pathways for blood cells and transport oxygen as well as nutrients into each individual organ. In the embryo, blood vessels develop simultaneously in many different places, then connect with each other and thus form a complex network. The starting point of vascular growth are the so-called endothelial cells. These can migrate in groups out from a vessel and form new tubes, the capillaries.
Prof. Markus Affolter’s team at the Biozentrum of the University of Basel uses the zebrafish as a model organism to investigate the development of blood vessels. In their current study, the scientists have shown that endothelial cells can migrate within vessel sprouts while remaining firmly attached to each other. If the cells were unable to remain attached, bleeding into the surrounding tissue would occur during vascularization.
Vascularization: constant rearrangement of endothelial cells
The transparency of the zebrafish embryo allows researchers to observe blood vessel formation live in the living organism. High-resolution time-lapse imaging of vascularization shows that the endothelial cells move over each other to form a capillary, thereby continuously rearranging their position in the newly forming vessel. Dr. Heinz-Georg Belting, head of the study, took a closer look at this process.
Migration and connection of vascular cells
During the rearrangement of the endothelial cells in the vessel, it is important that the cells elongate and migrate while constantly maintaining cell-cell junctions. The adhesion protein VE-cadherin and the cell skeleton play a crucial role in this process. “These two players must work closely together during these active cell movements,” says Belting. “The cytoskeleton takes the first step; it ensures the elongation of the cell. VE-cadherin then anchors the cell protrusions to the neighboring cell. An additional protein finally stabilizes the newly formed endothelial cell junction. This repetitive process enables the cell to slowly creep forward.” This mechanism works like a zipper, as soon as the cell has moved a little, the gap to the adjacent endothelial cell is closed.
Plasticity ensures growth and flexibility
The fact that the endothelial cells are very motile during blood vessel formation and yet always stay firmly connected ensures the plasticity of the vessel while maintaining its stability. “The ability of endothelial cells to recognize each other, to migrate and to form cell junctions prevents damage during growth. Furthermore, the blood vessels are flexible to respond to different conditions, such as fluctuations in blood pressure,” says Belting “This plasticity also plays a role in wound healing, inflammation and immune response.”
Prof. Dr. Markus Affolter, University of Basel, Biozentrum, tel. +41 61 207 20 72, email: markus.affolter@unibas.ch
Dr. Katrin Bühler, University of Basel, Biozentrum, Communications, Tel. +41 61 207 09 74, email: katrin.buehler@unibas.ch
Ilkka Paatero, Loïc Sauteur, Minkyoung Lee, Anne K. Lagendijk, Daniel Heutschi, Cora Wiesner, Camilo Gúzman, Dimitri Bieli, Benjamin M. Hogan, Markus Affolter & Heinz-Georg Belting
Junction-based lamellipodia drive endothelial cell rearrangements in vivo via a VE-cadherin-F-actin based oscillatory cell-cell interaction
Nature Communications (2018), doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-05851-9
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.unibas.chAll latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Silicon Carbide Innovation Alliance to drive industrial-scale semiconductor work
Known for its ability to withstand extreme environments and high voltages, silicon carbide (SiC) is a semiconducting material made up of silicon and carbon atoms arranged into crystals that is…

New SPECT/CT technique shows impressive biomarker identification
…offers increased access for prostate cancer patients. A novel SPECT/CT acquisition method can accurately detect radiopharmaceutical biodistribution in a convenient manner for prostate cancer patients, opening the door for more…

How 3D printers can give robots a soft touch
Soft skin coverings and touch sensors have emerged as a promising feature for robots that are both safer and more intuitive for human interaction, but they are expensive and difficult…





















