Improved characterization of nanoparticle clusters for EHS and biosensors research
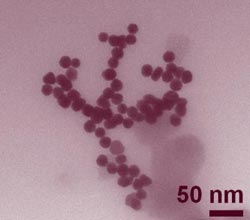
Clusters of roughly 30-nanometer gold nanoparticles imaged by transmission electron microscopy. (Color added for clarity.)<br>Credit: Keene, FDA<br><br>
Toxicity, the persistence of the nanomaterials in the environment, their efficacy as biosensors and, for that matter, the accuracy of experiments to measure these factors, are all known to be affected by agglomeration and cluster size. Recent work* at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) offers a way to measure accurately both the distribution of cluster sizes in a sample and the characteristic light absorption for each size. The latter is important for the application of nanoparticles in biosensors.
A good example of the potential application of the work, says NIST biomedical engineer Justin Zook, is in the development of nanoparticle biosensors for ultrasensitive pregnancy tests. Gold nanoparticles can be coated with antibodies to a hormone** produced by an embryo shortly after conception. Multiple gold nanoparticles can bind to each hormone, forming clusters that have a different color from unclustered gold nanoparticles. But only certain size clusters are optimal for this measurement, so knowing how light absorbance changes with cluster size makes it easier to design the biosensors to result in just the right sized clusters.
The NIST team first prepared samples of gold nanoparticles—a nanomaterial widely used in biology—in a standard cell culture solution, using their previously developed technique for creating samples with a controlled distribution of sizes***. The particles are allowed to agglomerate in gradually growing clusters and the clumping process is “turned off” after varying lengths of time by adding a stabilizing agent that prevents further agglomeration.
They then used a technique called analytical ultracentrifugation (AUC) to simultaneously sort the clusters by size and measure their light absorption. The centrifuge causes the nanoparticle clusters to separate by size, the smaller, lighter clusters moving more slowly than the larger ones. While this is happening, the sample containers are repeatedly scanned with light and the amount of light passing through the sample for each color or frequency is recorded. The larger the cluster, the more light is absorbed by lower frequencies. Measuring the absorption by frequency across the sample containers allows the researchers both to watch the gradual separation of cluster sizes and to correlate absorbed frequencies with specific cluster sizes.
Most previous measurements of absorption spectra for solutions of nanoparticles were able only to measure the bulk spectra—the absorption of all the different cluster sizes mixed together. AUC makes it possible to measure the quantity and distribution of each nanoparticle cluster without being confounded by other components in complex biological mixtures, such as proteins. The technique previously had been used only to make these measurements for single nanoparticles in solution. The NIST researchers are the first to show that the procedure also works for nanoparticle clusters.
* J.M. Zook, V. Rastogi, R.I. MacCuspie, A.M. Keene and J. Fagan. Measuring agglomerate size distribution and dependence of localized surface plasmon resonance absorbance on gold nanoparticle agglomerate size using analytical ultracentrifugation. ACS Nano, Articles ASAP (As Soon As Publishable). Publication Date (Web): Sept. 3, 2011 DOI: 10.1021/nn202645b.
** HCG: Human chorionic gonadotropin.
*** See J.M. Zook, R.I. MacCuspie, L.E. Locascio, M.D. Halter and J.T. Elliott. Stable nanoparticle aggregates/agglomerates of different sizes and the effect of their size on hemolytic cytotoxicity. Nanotoxicology, published online Dec. 13, 2010 (DOI: 10.3109/17435390.2010.536615) and the Feb. 2, 2011, NIST Tech Beat article, “NIST Technique Controls Sizes of Nanoparticle Clusters for EHS Studies,” at www.nist.gov/public_affairs/tech-beat/tb20110202.cfm#nanoparticles.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.nist.govAll latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Superradiant atoms could push the boundaries of how precisely time can be measured
Superradiant atoms can help us measure time more precisely than ever. In a new study, researchers from the University of Copenhagen present a new method for measuring the time interval,…

Ion thermoelectric conversion devices for near room temperature
The electrode sheet of the thermoelectric device consists of ionic hydrogel, which is sandwiched between the electrodes to form, and the Prussian blue on the electrode undergoes a redox reaction…

Zap Energy achieves 37-million-degree temperatures in a compact device
New publication reports record electron temperatures for a small-scale, sheared-flow-stabilized Z-pinch fusion device. In the nine decades since humans first produced fusion reactions, only a few fusion technologies have demonstrated…





















