How the cholera bacterium survives water predators
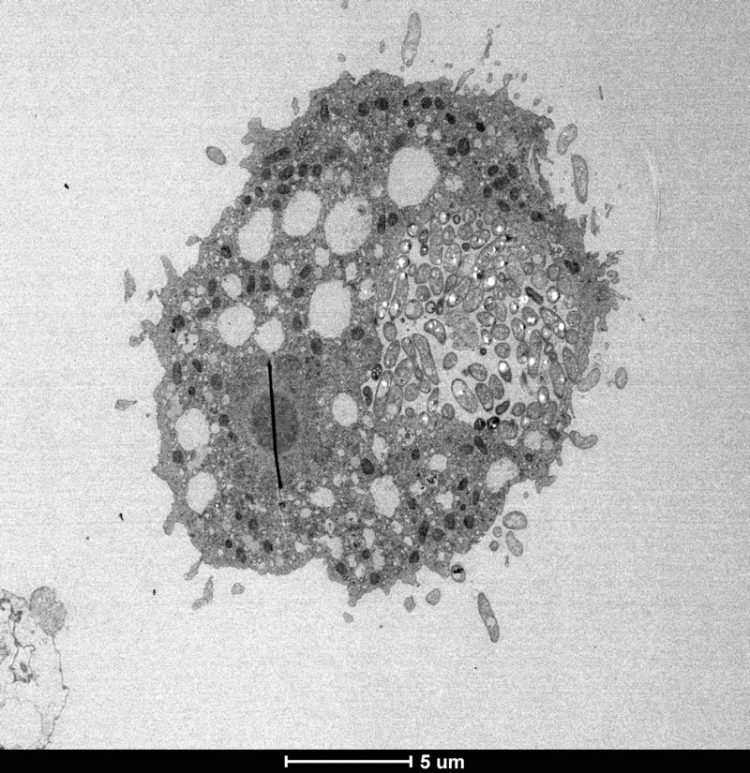
Electron micrograph of the cholera-causing pathogen inside an aquatic amoeba. Credit: Blokesch lab and BioEM facility (EPFL)
One of the ways the pathogen defends itself against predatory aquatic amoebas involves “hitchhiking” them and hiding inside the amoeba. Once there, the bacterium resists digestion and establishes a replication niche within the host's osmoregulatory organelle. This organelle is essential for the amoeba to balance its internal water pressure with the pressure exerted by the environment.
In a new study, the group of Melanie Blokesch at EPFL in collaboration with the BioEM facility headed by Graham Knott has deciphered the molecular mechanisms that V. cholerae uses to colonize aquatic amoebas.
The researchers demonstrated that the pathogen uses specific features that allow it to maintain its intra-amoebal replication niche and to ultimately escape from the succumbed host. Several of these features, including extracellular enzymes and motility, are considered minor virulence factors as they also play a role in human disease.
The study suggests that the aquatic milieu provides a training ground for V. cholerae and that adaptation towards amoebal predators might have contributed to V. cholerae's emergence as a major human pathogen.
“We are quite excited about these new data, as they support the hypothesis that predation pressure can select for specific features that might have dual roles – in the environment and within infected humans,” says Blokesch. She also highlights that continuous funding by the ERC (StG & CoG) has been crucial for this project, “as studying the environmental lifestyle of the pathogen is a bit outside the mainstream research on pathogenesis”.
###
Reference
Charles Van der Henst, Audrey Sophie Vanhove, Natália Carolina Drebes Dörr, Sandrine Stutzmann, Candice Stoudmann, Stéphanie Clerc, Tiziana Scrignari, Catherine Maclachlan, Graham Knott, Melanie Blokesch. Molecular insights into Vibrio cholerae's intra-amoebal host-pathogen interactions. Nature Communications 27 August 2018. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-05976-x
Media Contact
More Information:
http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-05976-xAll latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Rocks with the oldest evidence yet of Earth’s magnetic field
The 3.7 billion-year-old rocks may extend the magnetic field’s age by 200 million years. Geologists at MIT and Oxford University have uncovered ancient rocks in Greenland that bear the oldest…

Decisive breakthrough for battery production
Storing and utilising energy with innovative sulphur-based cathodes. HU research team develops foundations for sustainable battery technology Electric vehicles and portable electronic devices such as laptops and mobile phones are…

Superradiant atoms could push the boundaries of how precisely time can be measured
Superradiant atoms can help us measure time more precisely than ever. In a new study, researchers from the University of Copenhagen present a new method for measuring the time interval,…





















