How plague pathogens trick the immune system
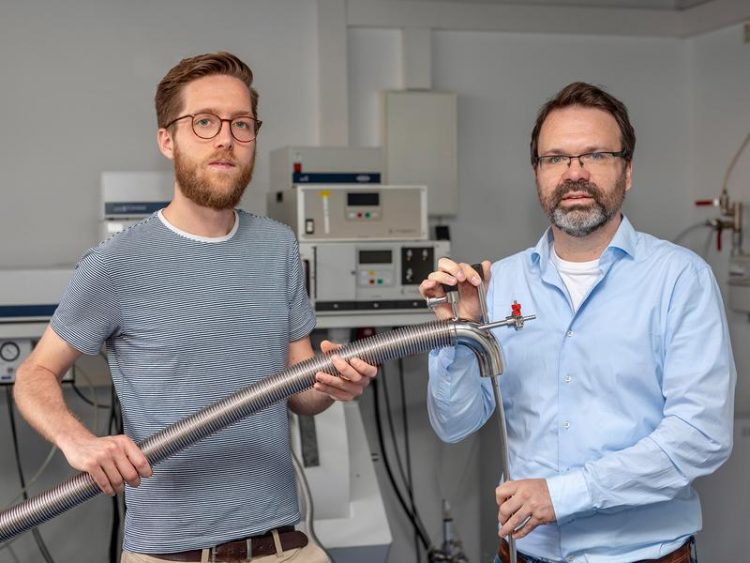

Prepare a measurement in the laboratory: Martin Peter (left) and Dr. Gregor Hagelüken (right) from the Institute of Physical and Theoretical Chemistry at the University of Bonn. © Photo: Hamed Alai
Yersinia also includes the plague pathogen, which caused fear and terror worldwide until the discovery of antibiotics. The major epidemics are over, but the World Health Organization (WHO) reported a total of 1451 deaths in 21 countries between 1978 and 1992.
Plague bacteria are also found in wild rodents. The transmission occurs mainly via fleas, but also via droplet infection. “Yersinia trick the macrophages of the immune system,” says Dr. Gregor Hagelüken from the Institute of Physical and Theoretical Chemistry at the University of Bonn.
The structural biologist has already done research in Yersinia as a PhD student at the Helmholtz Centre for Infection Research in Braunschweig. The special feature of the plague pathogens is a kind of syringe with which they inject the YopO and some other enzymes into the macrophages of the immune system.
However, YopO only becomes active when it binds to the actin of the scavenger cell. Normally, the structural protein actin helps the phagocyte to form protrusions with which it flows around the pathogens and then disolves them into small pieces. During this process, the macrophage calls for help from other defense cells.
YopO disrupts the communication of the immune system
“As soon as YopO has bound to the actin, however, it helps to disrupt communication within the macrophage – it can no longer attack,” reports Hagelüken. “The Yersinia remain ultimately undisturbed.” Researchers have been wondering for quite some time how YopO is activated by binding to actin, thus turning on the switch for the dramatic progression. “Scientists at Oxford University and the National University of Singapore deciphered the structure of the actin-bound YopO as early as 2015,” reports Hagelükens colleague and lead author Martin F. Peter. However, the structure was a kind of “still image”: it was not recognizable how the YopO changes its shape when it binds to the actin.
“Enzymes are not stiff structures but have several mobile `hinges´ with which they can change their shape,” explains Hagelüken. The researchers wanted to take two “snapshots”: One of YopO alone and in a second pass one of the YopO/actin complex. These “before and after images” should show how the two partners change their shape as a result of the complex formation. “This idea was a challenge because the normal method of crystal structure analysis did not work with the free YopO. As it turns out, it is too flexible to form ordered crystals,” says Peter.
Latest tools for structure elucidation
The scientists at the University of Bonn therefore used several instruments from the structural elucidation toolbox. Together with Dr. Dmitri Svergun from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory in Hamburg, they used the PETRA III electron accelerator of the German Electron Synchrotron DESY. “The extremely intense and focused X-rays can be used to study the overall structure and structural changes of enzymes dissolved in water with the aid of small-angle X-ray scattering,” said Svergun.
In addition, the researchers attached spin markers to certain positions of YopO and actin. These function like survey points in the landscape at which, for example, the exact location of a property can be determined. “Using the spin markers, we can use a molecular ruler – the PELDOR method – to measure the nanometer distances between these positions and thus determine how YopO and actin change shape,” reports Hagelüken. So far it has been presumed that YopO performs a folding movement like scissors as soon as it binds to actin. “Our results strongly indicate, however, that it is not a larger movement, but many small ones, with which YopO enters the active state,” says Peter.
Towards tailor-made substances
If detected in time, the plague can be cured well with antibiotics. “However, bacteria can become resistant if antibiotics are used frequently, which means that the drugs no longer work properly,” says Hagelüken. If the basic processes of pathogens with which they outwit the immune system are better understood, it might also be possible to develop more targeted, tailor-made substances to inhibit them.
Dr. Gregor Hagelüken
Institute of Physical and Theoretical Chemistry
University of Bonn
Tel. +49-228-733830
eMail: hagelueken@pc.uni-bonn.de
Martin F. Peter, Anne T. Tuukkanen, Caspar A. Heubach, Alexander Selsam, Fraser G. Duthie, Dmitri I. Svergun, Olav Schiemann, and Gregor Hagelueken: Studying Conformational Changes of the Yersinia Type-III-Secretion Effector YopO in Solution by Integrative Structural Biology, Journal “Structure”, DOI: 10.1016/j.str.2019.06.007
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.uni-bonn.de/All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Ion thermoelectric conversion devices for near room temperature
The electrode sheet of the thermoelectric device consists of ionic hydrogel, which is sandwiched between the electrodes to form, and the Prussian blue on the electrode undergoes a redox reaction…

Zap Energy achieves 37-million-degree temperatures in a compact device
New publication reports record electron temperatures for a small-scale, sheared-flow-stabilized Z-pinch fusion device. In the nine decades since humans first produced fusion reactions, only a few fusion technologies have demonstrated…
Innovative microscopy demystifies metabolism of Alzheimer’s
Researchers at UC San Diego have deployed state-of-the art imaging techniques to discover the metabolism driving Alzheimer’s disease; results suggest new treatment strategies. Alzheimer’s disease causes significant problems with memory,…





















