How do our cells respond to stress?
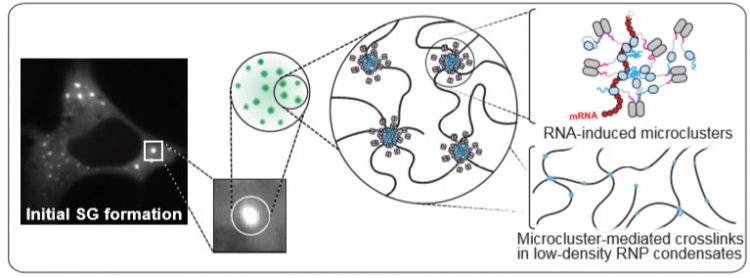
Model representing the behavior of the protein G3BP under stress: RNA molecules bind to G3BP, allowing multiple interactions that promote the clustering of G3BP and the assembly of dynamic stress granules (SG). The image on the left shows a cell in which stress granules were labeled with a fluorescent dye. The schematic on the right gives insight into the molecular structure and organization of stress granules. © Biotec
Cells are often exposed to stressful conditions that can be life threatening, such as high temperatures or toxins. Fortunately, our cells are masters of stress management with a powerful response program: they cease to grow, produce stress-protective factors, and form large structures, which are called stress granules.
Scientists at the Biotechnology Center (BIOTEC) of the TU Dresden and the Max Planck Institute of Molecular Cell Biology and Genetics (MPI-CBG), together with partners in Heidelberg and St. Louis (USA) have investigated how these mysterious structures assemble and dissolve, and what may cause their transition into a pathological state as observed in neurodegenerative diseases such as ALS (amyotrophic lateral sclerosis).
Their results were published in the renowned scientific journal Cell.
ALS is a hitherto incurable disease of the central nervous system in which the motor neurons – nerve cells responsible for the muscles movement – gradually die. Do stress granules play a role in this process?
Stress granules are formed in the cytoplasm of the cell and assemble from a large number of macromolecular components such as messenger RNAs and RNA-binding proteins. Stress granules usually disassemble when the stress subsides, a process which is promoted by the dynamic nature of stress granules. However, a hallmark of ALS is the presence of non-dynamic, persistent forms of stress granules.
“In ALS, patients suffer from muscle weakness and paralysis. Stress granule-containing motor neurons slowly degenerate, causing a progressive loss of motor functions. We need to better understand the complex biology of stress granules in order to design and develop future therapeutic strategies that counteract the course of the disease. But the complex environment of the cells within an organism makes this difficult,” explains Dr. Titus Franzmann, one of the senior authors of the publication.
In order to systematically test their hypotheses about the assembly of stress granules and the pathology causing molecular changes, the scientists developed a controlled environment using an in vitro system with purified components that allowed the recreation of stress granules in a test tube. They observed stress granule assembly step by step and characterized the critical factors underlying their dynamics.
“Stress granules have a very complex structure. Nevertheless, their formation depends primarily on the behavior of a single protein – the RNA-binding protein G3BP,” says Dr. Jordina Guillén-Boixet, one of the first authors of the study.
“This protein undergoes a critical structural change: Under non-stress conditions G3BP adopts a compact state that does not allow stress granules to assemble. But under stress, RNA molecules bind to G3BP allowing multiple interactions that promote the assembly of dynamic stress granules. The subsequent transition from dynamic into non-dynamic state, which may be caused for example by prolonged stress, may trigger the death of the motor neurons, as we can observe in the disease ALS.”
The research project was initiated in 2015 and led by the Alberti research group at TU Dresden´s BIOTEC. The close co-operation of 23 scientists from the TU Dresden, the Max Planck Institute of Molecular Cell Biology and Genetics in Dresden, the European Molecular Biology Laboratory in Heidelberg and the Washington University in St. Louis (USA) was central for the success of the project.
Prof. Simon Alberti: “There is a number of remaining questions. Our experimental system at BIOTEC is now available for further testing and will be central to developing new diagnostics and therapeutics to combat neurodegenerative diseases such as ALS.”
The research project was funded by the European Research Council (ERC), the Human Frontiers Science Program (HFSP), the European Molecular Biology Organization (EMBO), the German Research Foundation (DFG), the Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) and the Joint Neurodegenerative Disease Research Program (JPND) of the EU.
The Biotechnology Center (BIOTEC) was founded in 2000 as a central scientific unit of the Technische Universität Dresden (TU Dresden) with the goal of combining modern approaches in molecular- and cell biology with the traditionally strong engineering in Dresden.
Since 2016 the BIOTEC is part of the central scientific unit “Center for Molecular and Cellular Bioengineering” (CMCB) of the TU Dresden. The BIOTEC is fostering developments in research and teaching within the Molecular Bioengineering research field and combines approaches in cell biology, biophysics and bioinformatics. It plays a central role within the research priority area Health Sciences, Biomedicine and Bioengineering of the TU Dresden.
www.tu-dresden.de/biotec
www.tu-dresden.de/cmcb
Prof. Simon Alberti
Tel.: +49 351 463-40236
simon.alberti@tu-dresden.de
Cell: „RNA-Induced Conformational Switching and Clustering of G3BP Drive Stress Granule Assembly by Condensation“, Authors: Jordina Guillén-Boixet, Andrii Kopach, Alex S. Holehouse, Sina Wittmann, Marcus Jahnel, Raimund Schlüßler, Kyoohyun Kim, Irmela R.E.A. Trussina, Jie Wang, Daniel Mateju, Ina Poser, Shovamayee Maharana, Martine Ruer-Gruß, Doris Richter, Xiaojie Zhang, Young-Tae Chang, Jochen Guck, Alf Honigmann, Julia Mahamid, Anthony A. Hyman, Rohit V. Pappu, Simon Alberti, Titus M. Franzmann
https://www.cell.com/cell/fulltext/S0092-8674(20)30342-1
https://doi.org/10.101/j.cell.2020.03.049
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Properties of new materials for microchips
… can now be measured well. Reseachers of Delft University of Technology demonstrated measuring performance properties of ultrathin silicon membranes. Making ever smaller and more powerful chips requires new ultrathin…

Floating solar’s potential
… to support sustainable development by addressing climate, water, and energy goals holistically. A new study published this week in Nature Energy raises the potential for floating solar photovoltaics (FPV)…

Skyrmions move at record speeds
… a step towards the computing of the future. An international research team led by scientists from the CNRS1 has discovered that the magnetic nanobubbles2 known as skyrmions can be…





















