DNA damage by ultrashort pulses of intense laser light
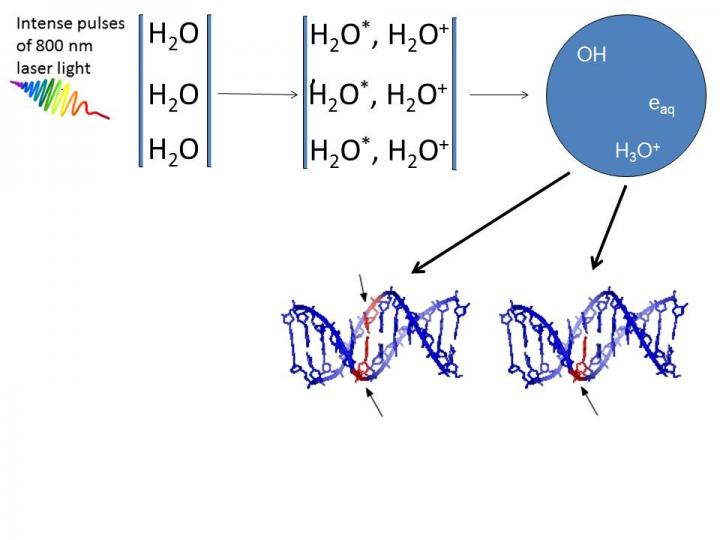
DNA damage caused by very low-energy electrons and OH-radicals formed upon irradiation of water by ultrashort pulses of very intense laser light. Credit: Deepak Mathur
High intensity femtosecond laser pulses were used to probe damage to aqueous DNA [1]. In propagating through the water medium, the intense light pulses cause H2O molecules to ionize and break-up, giving rise to low-energy electrons and OH-radicals. Both are responsible for producing breaks in DNA strands. Infact, earlier work carried out by the same team [2, 3] showed that OH radicals were four times more likely than electrons to produce double strand breaks in DNA.
A collaborative project between TIFR Mumbai, the Centre for Excellence in Basic Sciences, Mumbai, and Manipal University, the experiments described in this new publication utilized different incident laser energies and various external focusing conditions to establish that DNA damage occurs in two distinct regimes. Interestingly, the numerical aperture of the focusing lens (the light-gathering ability of the lens) delineates the two regimes. This permits optical control to be exercised over the extent of DNA damage by simply varying the focal length of the focusing lens.
“The experimental technique of generating, in situ, slow electrons and radicals within aqueous media has important implications in different scenarios where the effects of non-ionizing radiation need to be probed under physiologically relevant conditions,” says Professor Deepak Mathur, senior scientist at TIFR Mumbai, and the lead scientist of this study.
It has been suggested that detrimental dose distributions within tissues that are irradiated by gamma radiation – one of the major difficulties in radiotherapy — might be avoided by use of femtosecond laser induced filamentation. This is due to ultrashort laser pulses, particularly in the infrared region, being spatially confined to volumes (~125 μm3) that are much smaller than what is possible to attain using contemporary clinical radiation sources. This is important for minimising damage to non-target tissues in the vicinity.
###
1. J. A. Dharmadhikari, A. K. Dharamdhikari, K. C. Kasuba, H. Bharambe, J. S. D'Souza, K. D. Rathod, and D. Mathur, Sci. Reports — in press
2. J. S. D'Souza et al., Phys. Rev. Letters 106 (2011) 118101,/p>
3. A. K. Dharmadhikari et al., Phys. Rev. Letters 112 (2014) 138105
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Properties of new materials for microchips
… can now be measured well. Reseachers of Delft University of Technology demonstrated measuring performance properties of ultrathin silicon membranes. Making ever smaller and more powerful chips requires new ultrathin…

Floating solar’s potential
… to support sustainable development by addressing climate, water, and energy goals holistically. A new study published this week in Nature Energy raises the potential for floating solar photovoltaics (FPV)…

Skyrmions move at record speeds
… a step towards the computing of the future. An international research team led by scientists from the CNRS1 has discovered that the magnetic nanobubbles2 known as skyrmions can be…





















