Brain Size Influences Development of Individual Cranial Bones
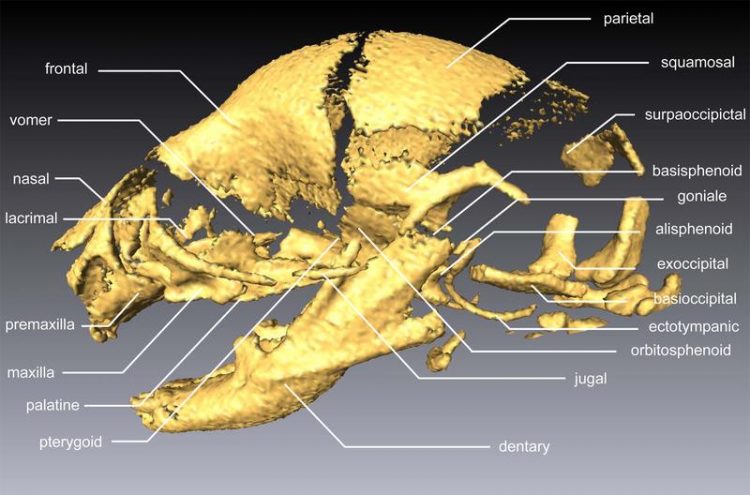
Skull bones of the Japanese field mouse Picture: UZH
Embryonic development in animals – except mice and rats – remains largely unexplored. For a research project at the University of Zurich, the embryos of 134 species of animal were studied non-invasively for the first time using microcomputer imaging, thus yielding globally unique data.
The embryos studied came from museum collections all over the world. The international team of researchers headed by Marcelo Sánchez-Villagra especially studied cranial formation and discovered that the individual cranial bones develop in different phases that are characteristic for the individual species. According to the study, which was published in the journal Nature communications, how the cranial bones develop in mammals also depends on brain size.
Brain size influences the timing of cranial development
The skulls of full-grown animals consist of many individual bones that have fused together. There are two types of bone: dermal and endochondral bones. Endochondral bones form from cartilaginous tissue, which ossifies in the course of the development. Dermal bones, on the other hand, are formed in the dermis. The majority of the skull consists of dermal bones. The bones inside the skull and the petrous bone, part of the temporal bone, however, are endochondral.
As Daisuke Koyabu, now at University of Tokyo, who conducted the studies while he was a post-doc under Sánchez-Villagra, was able to demonstrate, the different bone types do not develop synchronously: Dermal cranial bones form before the endochondrals. According to Sánchez-Villagra, this indicates that the individual bones form based on a precisely defined, coordinated schedule that is characteristic for every species of animal and enables conclusions to be drawn regarding their evolutionary relationships in the tree of animal life.
The researchers also discovered that individual bones in the area around the back of the head have changed their development plan in the course of evolution. “The development of larger brains in mammals triggered the changes observed in the development of bone formation,” Sánchez-Villagra.
Mammals: masticatory apparatus first
With the aid of quantitative methods and evolutionary trees, the researchers ultimately reconstructed the embryonic cranial development of the last common ancestors of all mammals, which lived 180 million years ago during the Jurassic period. As with the majority of mammals, its cranial development began with the formation of the masticatory apparatus bones.
Literature:
Daisuke Koyabu, Ingmar Werneburg, Naoki Morimoto, Christoph E. Zollikofer, Analia M. Forasiepi, Hideki Endo, Junpei Kimura, Stoshi D. Ohdachi, Son Ngyuen Truong, Marcelo R. Sánchez-Villagra, Mammalian skull heterochrony reveals modular evolution and a link between cranial development and brain size. Nature communications. April 4, 2014, doi: 10.1038/ncomms4625
Contact:
Prof. Dr. Marcelo R. Sánchez-Villagra
Paläontologisches Institut und Museum
Universität Zürich
E-Mail: m.sanchez@pim.uzh.ch
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Bringing bio-inspired robots to life
Nebraska researcher Eric Markvicka gets NSF CAREER Award to pursue manufacture of novel materials for soft robotics and stretchable electronics. Engineers are increasingly eager to develop robots that mimic the…

Bella moths use poison to attract mates
Scientists are closer to finding out how. Pyrrolizidine alkaloids are as bitter and toxic as they are hard to pronounce. They’re produced by several different types of plants and are…

AI tool creates ‘synthetic’ images of cells
…for enhanced microscopy analysis. Observing individual cells through microscopes can reveal a range of important cell biological phenomena that frequently play a role in human diseases, but the process of…





















