Bioengineers: Matrix stiffness is an essential tool in stem cell differentiation
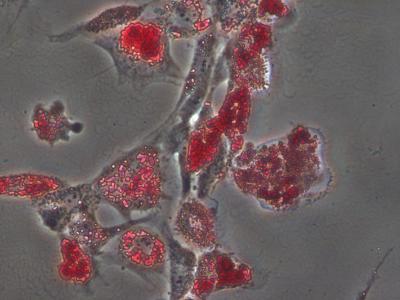
Cells grown on hydrogels of the same stiffness all display fat cell markers and deform the underlying matrix material the same way. Credit: Adam Engler, UC San Diego Jacobs School of Engineering
When placed in a dish of a very stiff material, or hydrogel, most stem cells become bone-like cells. By comparison, soft materials tend to steer stem cells into soft tissues such as neurons and fat cells.
The research team, led by bioengineering professor Adam Engler, also found that a protein binding the stem cell to the hydrogel is not a factor in the differentiation of the stem cell as previously suggested. The protein layer is merely an adhesive, the team reported Aug. 10 in the advance online edition of the journal Nature Materials.
Their findings affirm Engler's prior work on the relationship between matrix stiffness and stem cell differentiations.
“What's remarkable is that you can see that the cells have made the first decisions to become bone cells, with just this one cue. That's why this is important for tissue engineering,” said Engler, a professor at the UC San Diego Jacobs School of Engineering.
Engler's team, which includes bioengineering graduate student researchers Ludovic Vincent and Jessica Wen, found that the stem cell differentiation is a response to the mechanical deformation of the hydrogel from the force exerted by the cell.
In a series of experiments, the team found that this happens whether the protein tethering the cell to the matrix is tight, loose or nonexistent. To illustrate the concept, Vincent described the pores in the matrix as holes in a sponge covered with ropes of protein fibers.
Imagine that a rope is draped over a number of these holes, tethered loosely with only a few anchors or tightly with many anchors. Across multiple samples using a stiff matrix, while varying the degree of tethering, the researchers found no difference in the rate at which stem cells showed signs of turning into bone-like cells.
The team also found that the size of the pores in the matrix also had no effect on the differentiation of the stem cells as long as the stiffness of the hydrogel remained the same.
“We made the stiffness the same and changed how the protein is presented to the cells (by varying the size of the pores and tethering) and ask whether or not the cells change their behavior,” Vincent said. “Do they respond only to the stiffness? Neither the tethering nor the pore size changed the cells.”
“We're only giving them one cue out of dozens that are important in stem cell differentiation,” said Engler. “That doesn't mean the other cues are irrelevant; they may still push the cells into a specific cell type. We have just ruled out porosity and tethering, and further emphasized stiffness in this process.”
The paper is “Interplay of matrix stiffness and protein tethering in stem cell differentiation,” by Jessica H. Wen, Ludovic G. Vincent, Alexander Fuhrmann, Yu Suk Choi, Kolin Hribar, Hermes Taylor-Weiner, Shaochen Chen and Adam J. Engler in the Departments of Bioengineering and NanoEngineering at UC San Diego Jacobs School of Engineering. Engler is also a researcher at the Sanford Consortium for Regenerative Medicine. His work is partially funded by the National Institutes of Health (DP02D006460).
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Superradiant atoms could push the boundaries of how precisely time can be measured
Superradiant atoms can help us measure time more precisely than ever. In a new study, researchers from the University of Copenhagen present a new method for measuring the time interval,…

Ion thermoelectric conversion devices for near room temperature
The electrode sheet of the thermoelectric device consists of ionic hydrogel, which is sandwiched between the electrodes to form, and the Prussian blue on the electrode undergoes a redox reaction…

Zap Energy achieves 37-million-degree temperatures in a compact device
New publication reports record electron temperatures for a small-scale, sheared-flow-stabilized Z-pinch fusion device. In the nine decades since humans first produced fusion reactions, only a few fusion technologies have demonstrated…





















