Biodegradable electronics
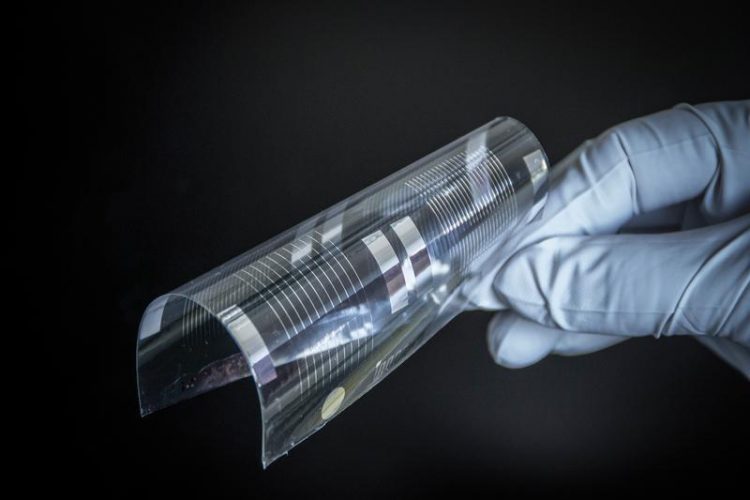
Biodegradable conductor structures on biodegradable polymer film © Fraunhofer FEP
Electronic devices that are completely broken down in a biological environment after a pre-defined operating life open up novel applications as well as ways for reducing their ecological footprint.
One enabling technology for such devices is the production of biodegradable conductive traces on biodegradable substrates using vacuum technologies. This technology was developed by Fraunhofer FEP.
A novel application area for these innovative electronic components for example is in the field of active medical implants that after expiration of their operating life are resorbed by tissue, thereby sparing the patient a second surgical intervention.
The Fraunhofer Gesellschaft e. V. is now funding the “bioElektron – Biodegradable Electronics for Active Implants” project through its in-house program (funding No. MAVO B31 301). The goal of the project is the development of essential components for biodegradable electronic parts that can be employed for example in an implant.
This includes in particular
– biodegradable conductor structures
– biodegradable electrodes for collecting electrical signals or delivering electrical stimulation
– biodegradable thin-film transistors and circuitry
– biodegradable barrier coatings as moisture and gas barriers, and electrical insulation layers
These elements will be monolithically integrated into a flexible thin-film device.
Conductor structures and organic thin-film transistors are being developed at Fraunhofer FEP using vacuum technology. Deposition of magnesium via thermal evaporation under high vacuum conditions is being used as an enabling technology for this purpose.
Magnesium is known for being a biodegradable and biologically compatible metal that is already employed in clinical environments as an absorbable implant material. The challenge consists of depositing this metal onto biodegradable polymer films that magnesium does not adhere sufficiently to under normal processing conditions. By suitably pre-treating the substrates using a combination of drying, plasma treatment, and utilization of seed layers, finely structured high-quality conductor structures have been produced.
“We are now prepared to discuss these results with interested partners from industry and the scientific community during productronica 2017 at the Silicon-Saxony joint booth (Hall B1, Booth B1-416) in order to be able to implement them in current practical applications”, explains Dr. Michael Hoffmann from Fraunhofer FEP and head of the bioElektron project.
Fraunhofer FEP at productronica 2017 (SEMICON und FlexEurope):
Trade-fair booth: Silicon-Saxony joint booth in Hall B1, Booth No. B1-416
Talks:
Wednesday, 15.11.2017, 2:35 pm, ICM 1st floor, Room 14c
„Biodegradable flexible conductor structures“, Dr. Michael Hoffmann, Fraunhofer FEP
Innovation Forum
Hall B2, next to booth no. 457 OE-A Organic and Printed Electronics Association
Wednesday, 15.11.2017, 3:00 pm, Hall B2 / 453
Session: Printed Electronics Insights: Advancing Wearables
Electronics and OLED lighting in textiles, Jan Hesse, Fraunhofer FEP
Thursday, 16.11.2017, 3:00 pm, Halle B2 / 453
Session: Printed Electronics Insights: Applications and New Developments
Ultra-thin glass as a substrate and encapsulant for bendable OLED devices fabricated in Roll-to-Roll, Dr. Stefan Mogck, Fraunhofer FEP
Press contact:
Mrs. Annett Arnold
Fraunhofer Institute for Organic Electronics, Electron Beam and Plasma Technology FEP
Phone +49 351 2586 333 | presse@fep.fraunhofer.de
Winterbergstraße 28 | 01277 Dresden | Germany | www.fep.fraunhofer.de
About bioELEKTRON:
https://www.fep.fraunhofer.de/en/ueber-uns/projekte/bioElektron.html
Link for the press release on the Fraunhofer FEP Website:
http://s.fhg.de/k5i
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Superradiant atoms could push the boundaries of how precisely time can be measured
Superradiant atoms can help us measure time more precisely than ever. In a new study, researchers from the University of Copenhagen present a new method for measuring the time interval,…

Ion thermoelectric conversion devices for near room temperature
The electrode sheet of the thermoelectric device consists of ionic hydrogel, which is sandwiched between the electrodes to form, and the Prussian blue on the electrode undergoes a redox reaction…

Zap Energy achieves 37-million-degree temperatures in a compact device
New publication reports record electron temperatures for a small-scale, sheared-flow-stabilized Z-pinch fusion device. In the nine decades since humans first produced fusion reactions, only a few fusion technologies have demonstrated…





















