Want bigger plants? Get to the root of the matter
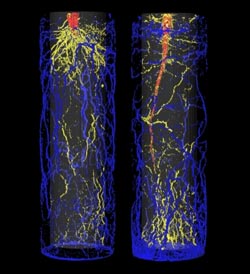
Left: This image shows the roots of a barley plant in a cylindrical pot imaged by MRI 44 days after sowing. Blue roots are in the outer 50 percent of the pot volume, yellow roots are in the inner 50 percent of the pot volume, the stem of the barley plant is in red. Credit: Jonas Bühler<br><br>Right: This image shows the roots of a sugar beet growing in a cylindrical pot, imaged by MRI 44 days after sowing. Roots in blue grew in the outer 50 percent volume of the pot, roots in yellow grew in the inner 50 percent pot volume, and the storage organ of the sugar beet is in red. Credit: Jonas Bühler<br>
From their 3-D MRI root scans, the researchers observed that potted plants quickly extend their roots to the pot's walls. It is likely that the plants use their roots to 'sense' the size of the pot, although the details of how the roots relay the message about the pot's size remain the plants' secret.
They also looked at 65 independent studies across a wide range of species including tomato, corn, pine tree, cactus, wheat, and cotton plants, and found that all species reach larger sizes when grown in a bigger pot. On average, doubling pot size allowed plants to grow 43% larger.
Dr Hendrik Poorter (Forschungszentrum Jülich, Germany) who led the study, said: “There has been commercial interest in seeing how small pots can be, but our aim was to see how big a pot needs to be to avoid affecting plant experiments.”
The work is relevant for gardeners too. Poorter added, “After this study, I immediately changed the pot size for all the plants I had in my house.”
To understand the pot size effect, the scientists looked at various aspects of the plants' growth. They found that the plants in smaller pots grew more slowly because of a decreased rate of photosynthesis. But, looking for causes for the decrease, the scientists ruled out limitations in water and nutrients and did not find any differences in the thickness of the leaves for plants in smaller pots. It is therefore unlikely that the plants use water and nutrient levels to sense the pot size, supporting the possibility that sensing happens another way, such as by the roots.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.fz-juelich.deAll latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Properties of new materials for microchips
… can now be measured well. Reseachers of Delft University of Technology demonstrated measuring performance properties of ultrathin silicon membranes. Making ever smaller and more powerful chips requires new ultrathin…

Floating solar’s potential
… to support sustainable development by addressing climate, water, and energy goals holistically. A new study published this week in Nature Energy raises the potential for floating solar photovoltaics (FPV)…

Skyrmions move at record speeds
… a step towards the computing of the future. An international research team led by scientists from the CNRS1 has discovered that the magnetic nanobubbles2 known as skyrmions can be…





















