Bacteria: Protein researchers decipher resistance mechanism
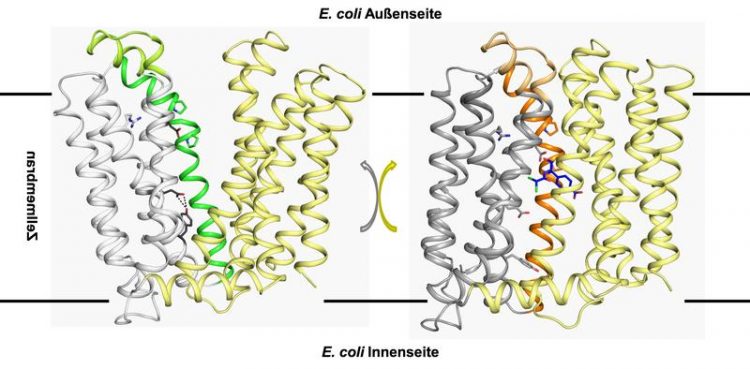
The protein MdfA is located in the cell membrane of E. coli. During the structural transformation of one structure into the other (and back), the antibiotic is pumped out of the cell. Milton Stubbs
Antibiotic resistance of bacteria is one of the most important medical issues of our time. Left unchecked, previously well-treatable bacterial diseases are at risk of taking such severe turns that patients might die.
“This is a real threat,” says Professor Milton T. Stubbs, Director of the Centre for Innovation Competence (ZIK) “HALOmem” where the work was conducted. According to Stubbs, who has been researching the biosynthesis of antibiotics for many years, the danger this poses means it is crucial to understand the mechanisms of antibiotic resistance.
The current study is the result of work by a junior research group at ZIK HALOmem, led at the time by Dr Mikio Tanabe. Tanabe is now an Associate Professor at the KEK Research Facility in Tsukuba, Japan. The group succeeded in isolating a membrane protein called MdfA from E. coli bacteria and were able to determine its molecular structure. The protein first had to be produced in the laboratory, isolated in its pure form and crystallised.
“Dealing with sensitive membrane proteins is a very complicated process. Optimal conditions must be maintained in the laboratory so that the protein remains stable and keeps its native structure,” explains Stubbs.
X-ray crystallography made it possible to visualise the structure of the material produced. Using this precise physical process, researchers are able to penetrate the Ångström range – one Ångström corresponds to one tenth of a nanometre, i.e. one ten billionth (10-10) of a metre, allowing researchers to work at a level at which individual atoms become visible. The ability to locate individual atoms in a molecule at this resolution holds the key to understanding how the protein works.
The process has revealed the three-dimensional structure of the membrane protein MdfA in the E. coli bacterium. The researchers from Halle utilised the results of a study that a rival group in China had recently published on the same protein and thereby succeeded in determining the mechanism that the membrane protein MdfA uses to help the bacterium become resistant.
The principle is reminiscent of a kind of pump mechanism. Although the drug is initially absorbed by the bacteria, it is ejected from the cell by MdfA before it becomes lethal to the bacteria.
“We assume that the mechanism discovered in this research applies to many other antibiotics,” explains Milton Stubbs. This information will also provide the basis for later practical applications. “It is not until we understand the mechanisms of how resistances develop that we can look for solutions to prevent them.”
The research paper has been published in the renowned journal “Nature Communications”. It is also one of the first research papers to be published under the umbrella of the new Charles Tanford Protein Centre at MLU. “Such success, of course, is a testament to our research location,” says Milton Stubbs.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.uni-halle.deAll latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Silicon Carbide Innovation Alliance to drive industrial-scale semiconductor work
Known for its ability to withstand extreme environments and high voltages, silicon carbide (SiC) is a semiconducting material made up of silicon and carbon atoms arranged into crystals that is…

New SPECT/CT technique shows impressive biomarker identification
…offers increased access for prostate cancer patients. A novel SPECT/CT acquisition method can accurately detect radiopharmaceutical biodistribution in a convenient manner for prostate cancer patients, opening the door for more…

How 3D printers can give robots a soft touch
Soft skin coverings and touch sensors have emerged as a promising feature for robots that are both safer and more intuitive for human interaction, but they are expensive and difficult…





















