Anti-Cancer Therapy Delivering Drug to an Entire Tumor Developed by KAIST Researchers
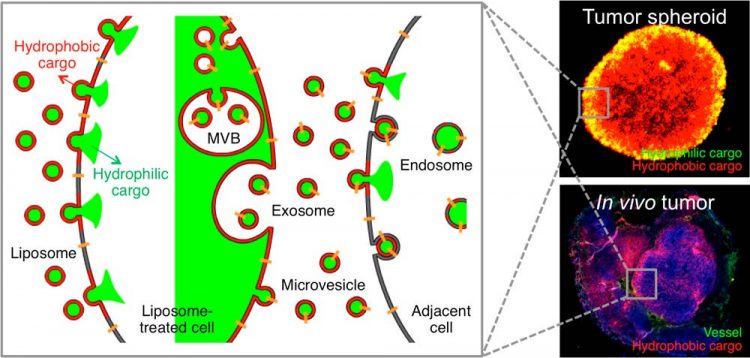
Incorporation of hydrophilic and hydrophobic compounds into membrane vesicles by engineering the parental cells via synthetic liposomes. Copyright: KAIST
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)’s Department of Bio and Brain Engineering Professor Ji-Ho Park and his team successfully developed a new highly efficacious anti-cancer nanotechnology by delivering anti-cancer drugs uniformly to an entire tumor. Their research results were published in Nano Letters online on March 31, 2015.
To treat inoperable tumors, anti-cancer medicine is commonly used. However, efficient drug delivery to tumor cells is often difficult, treating an entire tumor with drugs even more so.
Using the existing drug delivery systems, including nanotechnology, a drug can be delivered only to tumor cells near blood vessels, leaving cells at the heart of a tumor intact. Since most drugs are injected into the bloodstream, tumor recurrence post medication is frequent.
Therefore, the team used liposomes that can fuse to the cell membrane and enter the cell. Once inside liposomes the drug can travel into the bloodstream, enter tumor cells near blood vessels, where they are loaded to exosomes, which are naturally occurring nanoparticles in the body. Since exosomes can travel between cells, the drug can be delivered efficiently into inner cells of the tumor.
Exosomes, which are secreted by cells that exist in the tumor microenvironment, is known to have an important role in tumor progression and metastasis since they transfer biological materials between cells. The research team started the investigation recognizing the possibility of delivering the anti-cancer drug to the entire tumor using exosomes.
The team injected the light-sensitive anti-cancer drug using their new delivery technique into experimental mice. The researchers applied light to the tumor site to activate the anti-cancer treatment and analyzed a tissue sample. They observed the effects of the anti-cancer drug in the entire tumor tissue.
The team’s results establish a ground-breaking foothold in drug delivery technology development that can be tailored to specific diseases by understanding its microenvironment. The work paves the way to more effective drug delivery systems for many chronic diseases, including cancer tumors that were difficult to treat due to the inability to penetrate deep into the tissue.
The team is currently conducting experiments with other anti-cancer drugs, which are being developed by pharmaceutical companies, using their tumor-penetrating drug delivery nanotechnology, to identify its effects on malignant tumors, which were difficult to penetrate with existing technology.
Professor Park said, “This research is the first to apply biological nanoparticles, exosomes that are continuously secreted and can transfer materials to neighboring cells, to deliver drugs directly to the heart of tumor.”
Associated links
KAIST press release
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.researchsea.comAll latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

“Nanostitches” enable lighter and tougher composite materials
In research that may lead to next-generation airplanes and spacecraft, MIT engineers used carbon nanotubes to prevent cracking in multilayered composites. To save on fuel and reduce aircraft emissions, engineers…

Trash to treasure
Researchers turn metal waste into catalyst for hydrogen. Scientists have found a way to transform metal waste into a highly efficient catalyst to make hydrogen from water, a discovery that…

Real-time detection of infectious disease viruses
… by searching for molecular fingerprinting. A research team consisting of Professor Kyoung-Duck Park and Taeyoung Moon and Huitae Joo, PhD candidates, from the Department of Physics at Pohang University…





















