A new toxin in Cholera bacteria discovered by scientists in Umeå
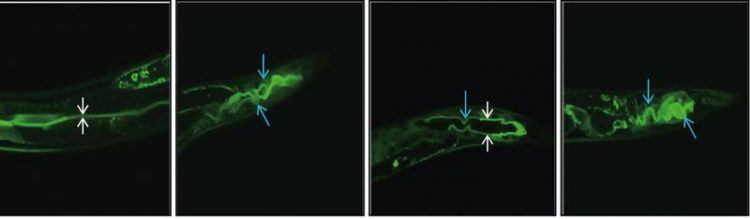
Fluorescence micrographs of the worm Caenorhabditis elegans infected with MakA toxin marked with green fluorescencent protein. The arrows show the twisted intestines Nature Communications Biology
The bacterium Vibrio cholerae was discovered more than 150 years ago but remains as one of the main causes of bacterial infectious disease globally, especially in low-income nations where it occurs endemic, and outbreaks of cholera disease can lead to major epidemics.
In addition to causing cholera disease characterized by very severe watery diarrhea, different variants of V. cholerae can cause, for example, wound infections and infections in the ear canal (ear inflammation). If the infection is reaching the bloodstream, it can lead to blood poisoning. Such variants of Vibrio bacteria are common in brackish water, but can be found both in freshwater and saltwater and are also present in such environments in our country.
Scientists from Umeå University have now discovered and characterised the structure and function of a so far unknown Vibrio toxin. A team led by Professor Sun Nyunt Wai at Department of Molecular Biology and MIMS used the worm Caenorhabditis elegans as a predatory host for the bacteria and identified by molecular genetic analysis the V. cholerae genes required for production and release of the new protein toxin, now called MakA.
“In addition to the toxicity of MakA demonstrated with C. elegans, our studies revealed that upon infection of Zebrafish the toxin caused damage in particular to the intestinal system,” explains Sun Nyunt Wai.
Sun Nyunt Wai and her colleagues were also curious about the details of the bacterial release mechanism of the newly discovered toxin from V. cholerae.
Vibrio cholerae is a motile bacterium, able to swim in fluids, driven by a rotating flagellum at the back of the cell. The scientists found that the flagellum of this bacterium not only is used as the mechanism for motility but also for the release of the MakA toxin.
“Using a combination of electron microscopy and light microscopy with molecular genetic methods we obtained evidence that this protein toxin is transported through the channel of the flagellum filamentous structure”, Sun Nyunt Wai explains.
This is the first time that scientists show how the flagellum functions as a secretion apparatus for a toxin from Vibrio cholerae.
Regarding the aim of these studies Sun Nyunt Wai explains: “In order to fully understand the disease-causing properties, and the distinctive ability of V. cholerae to survive and spread in different environments, it is important to study not only factors important for colonization and growth in human infections. Our aim was to also identify factors that may have evolved to be decisive for the environmental impact of the bacterium in competition with other microorganisms and for survival where there are predatory organisms. Our findings about MakA demonstrate that it is a novel cytotoxin affecting both vertebrate and invertebrate hosts.”
In the future, Sun Nyunt Wai and her colleagues would like to study also the effects and role of the MakA toxin in natural systems.
“Of course, we also want to find out if MakA might be responsible for some of the fish deaths in natural environments, and e.g in fisheries”. An immunization of the breeding fish against MakA would be a nice solution instead of treating the fish with antibiotics.
Scientists (and their affiliations) involved in the study:
Mitesh Dongre, Bhupender Singh, Kyaw Min Aung, Per Larsson, Regina Miftakova, Jenny L. Persson, Bernt Eric Uhlin, Sun Nyunt Wai (Department of Molecular Biology and The Laboratory for Molecular Infection Medicine Sweden (MIMS, mims.umu.se), Umeå Centre for Microbial Research (UCMR, www.ucmr.umu.se) Umeå University)
Karina Persson (Department of Chemistry and UCMR, Umeå University)
Simon Tuck, Jonas von Hofsten (Umeå Centre for Molecular Medicine (UCMM, ucmm.umu.se) and UCMR, Umeå University)
Fatemeh Askarian, Mona Johannessen (Department of Medical Biology, UiT- The Arctic University of Norway, Tromsø, Norway
Mark Erhardt (Helmholtz Centre for Infection Research, Braunschweig, Germany)
The orginal publication:
Mitesh Dongre, Bhupender Singh, Kyaw Min Aung, Per Larsson, Regina Miftakhova, Karina Persson, Fatemeh Askarian, Mona Johannessen, Jonas von Hofsten, Jenny L. Persson, Marc Erhardt, Simon Tuck, Bernt Eric Uhlin & Sun Nyunt Wai (2018). Flagella-mediated secretion of a novel Vibrio cholerae cytotoxin affecting both vertebrate and invertebrate hosts. Communications Biology 1:159; DOI: 10.1038/s42003-018-0065 (www.nature.com/commsbio )
Contact:
Professor Sun Nyunt Wai, Department of Molecular Biology and
The Laboratory for Molecular Infection Medicine Sweden (MIMS)
Umeå Centre for Microbial Research (UCMR)
Umeå University
sun.nyunt.wai@umu.se
Phone: +46 (0)90-785 67 04
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.vr.seAll latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

High-energy-density aqueous battery based on halogen multi-electron transfer
Traditional non-aqueous lithium-ion batteries have a high energy density, but their safety is compromised due to the flammable organic electrolytes they utilize. Aqueous batteries use water as the solvent for…

First-ever combined heart pump and pig kidney transplant
…gives new hope to patient with terminal illness. Surgeons at NYU Langone Health performed the first-ever combined mechanical heart pump and gene-edited pig kidney transplant surgery in a 54-year-old woman…

Biophysics: Testing how well biomarkers work
LMU researchers have developed a method to determine how reliably target proteins can be labeled using super-resolution fluorescence microscopy. Modern microscopy techniques make it possible to examine the inner workings…





















