A New Discovery in the Fight against Cancer: Tumor Cells Switch to a Different Mode
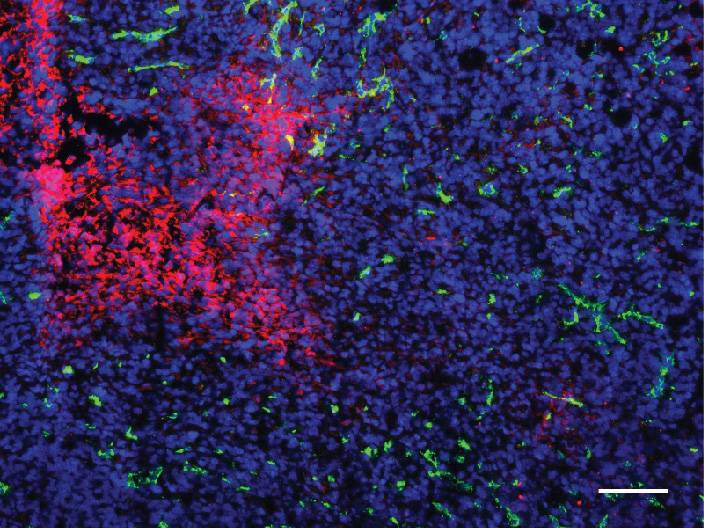
Following anti-angiogenic therapy, tumors develop regions containing no blood vessels (green) and therefore no oxygen (red). The tumor cells are made visible by dyeing the nuclei blue. University of Basel, Department of Biomedicine
One in three people still develop cancer at some point in their lives, and even now half of these cases result in death. There is therefore a demand for new approaches in the fight against cancer. Today, it is common knowledge that the disease develops in a series of stages. One of these stages, tumor angiogenesis, involves the formation of new blood vessels to supply oxygen and nutrients to the growing tumor.
Understanding the basics of how cancer forms has led to the development of increasingly targeted techniques for combating tumors: today, medications can simultaneously inhibit several signaling pathways that regulate tumor angiogenesis.
Understanding of the molecular basis for this process has paved the way for the routine application of specific therapies in the clinical setting: for example, so-called anti-angiogenic therapy can be used to prevent the formation of the blood vessels that supply tumors.
But this usually achieves only temporary success. Tumor growth is initially slowed or even stopped for a time; however, as the treatment goes on, the tumors begins to develop resistance to these therapies – and they start to grow again.
“An unexpected observation”
Now, the research group lead by Prof. Gerhard Christofori of the Department of Biomedicine at the University of Basel and University Hospital Basel has shown that, although the latest medications are effective at preventing blood vessel formation, the tumors can continue growing even without a supply of new blood vessels – an unexpected observation, as the researchers report in the publication.
Analysis of this finding from a biochemical and molecular genetic perspective revealed that the tumor cells convert to a different type of metabolism: they no longer produce energy using oxygen delivered via the blood vessels – but instead switch over to glycolysis, a form of anaerobic energy production. The lactic acid formed as a result is delivered to cells that are still receiving sufficient oxygen and that can use the lactic acid, together with the oxygen, to produce energy.
New therapies possible
The research group also showed that this specific mode of metabolism – and therefore the tumor’s growth – can be interrupted, namely by inhibiting anaerobic energy production or transport of the lactic acid. “Our findings open up new approaches for the optimization of anti-angiogenic therapies and for inhibiting tumor growth effectively in the long term,” says co-author Christofori about the group’s results.
Original paper
Laura Pisarsky, Ruben Bill, Ernesta Fagiani, Sarah Dimeloe, Ryan William Goosen, Jörg Hagmann, Christoph Hess, and Gerhard Christofori
Targeting Metabolic Symbiosis to Overcome Resistance to Anti-angiogenic Therapy
Cell Reports (2016), doi:
Further information
Prof. Dr. Gerhard Christofori, Department of Biomedicine at the University of Basel and University Hospital Basel, tel. +41 61 267 35 62, email: gerhard.christofori@unibas.ch
https://www.unibas.ch/en/News-Events/News/Uni-Research/A-New-Discovery-in-the-Fi…
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Silicon Carbide Innovation Alliance to drive industrial-scale semiconductor work
Known for its ability to withstand extreme environments and high voltages, silicon carbide (SiC) is a semiconducting material made up of silicon and carbon atoms arranged into crystals that is…

New SPECT/CT technique shows impressive biomarker identification
…offers increased access for prostate cancer patients. A novel SPECT/CT acquisition method can accurately detect radiopharmaceutical biodistribution in a convenient manner for prostate cancer patients, opening the door for more…

How 3D printers can give robots a soft touch
Soft skin coverings and touch sensors have emerged as a promising feature for robots that are both safer and more intuitive for human interaction, but they are expensive and difficult…





















