Graphene-based film can be used for efficient cooling of electronics
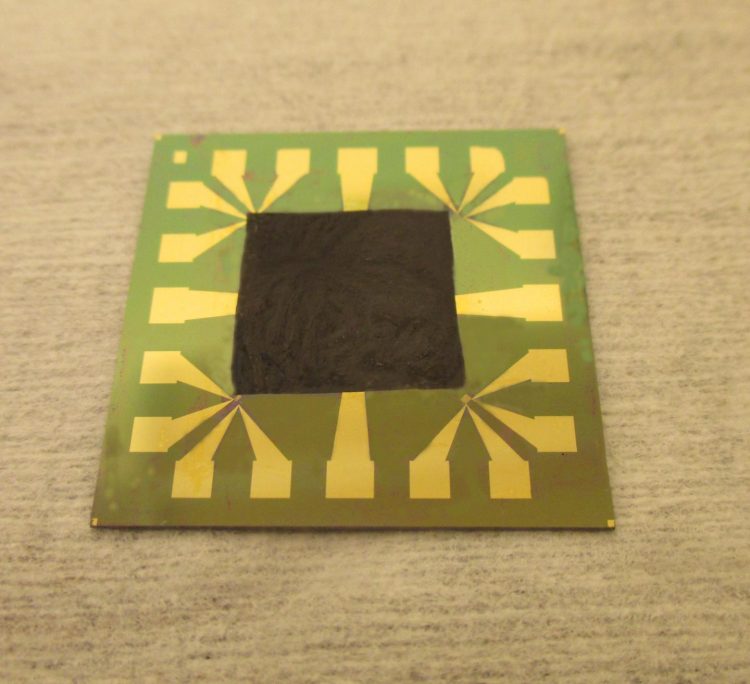
This is graphene-based film on an electronic component with high heat intensity. Credit: Johan Liu / Chalmers University of Technology
Researchers at Chalmers University of Technology have developed a method for efficiently cooling electronics using graphene-based film. The film has a thermal conductivity capacity that is four times that of copper.
Moreover, the graphene film is attachable to electronic components made of silicon, which favours the film's performance compared to typical graphene characteristics shown in previous, similar experiments.
Electronic systems available today accumulate a great deal of heat, mostly due to the ever-increasing demand on functionality. Getting rid of excess heat in efficient ways is imperative to prolonging electronic lifespan, and would also lead to a considerable reduction in energy usage. According to an American study, approximately half the energy required to run computer servers, is used for cooling purposes alone.
A couple of years ago, a research team led by Johan Liu, professor at Chalmers University of Technology, were the first to show that graphene can have a cooling effect on silicon-based electronics. That was the starting point for researchers conducting research on the cooling of silicon-based electronics using graphene.
“But the methods that have been in place so far have presented the researchers with problems”, Johan Liu says. “It has become evident that those methods cannot be used to rid electronic devices off great amounts of heat, because they have consisted only of a few layers of thermal conductive atoms. When you try to add more layers of graphene, another problem arises, a problem with adhesiveness. After having increased the amount of layers, the graphene no longer will adhere to the surface, since the adhesion is held together only by weak van der Waals bonds.”
“We have now solved this problem by managing to create strong covalent bonds between the graphene film and the surface, which is an electronic component made of silicon,” he continues.
The stronger bonds result from so-called functionalisation of the graphene, i.e. the addition of a property-altering molecule. Having tested several different additives, the Chalmers researchers concluded that an addition of (3-Aminopropyl) triethoxysilane (APTES) molecules has the most desired effect. When heated and put through hydrolysis, it creates so-called silane bonds between the graphene and the electronic component (see picture).
Moreover, functionalisation using silane coupling doubles the thermal conductivity of the graphene. The researchers have shown that the in-plane thermal conductivity of the graphene-based film, with 20 micrometer thickness, can reach a thermal conductivity value of 1600 W/mK, which is four times that of copper.
“Increased thermal capacity could lead to several new applications for graphene,” says Johan Liu. “One example is the integration of graphene-based film into microelectronic devices and systems, such as highly efficient Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs), lasers and radio frequency components for cooling purposes. Graphene-based film could also pave the way for faster, smaller, more energy efficient, sustainable high power electronics.”
###
Facts about the research:
The results were recently published in the renowned journal Advanced Functional Materials:
Improved Heat Spreading Performance of Functionalized Graphene in Microelectronic Device Application
The research was conducted in collaboration with Shanghai University in China, Ecole Centrale Paris and EM2C – CNRS in France, and SHT Smart High Tech in Sweden.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Information Technology
Here you can find a summary of innovations in the fields of information and data processing and up-to-date developments on IT equipment and hardware.
This area covers topics such as IT services, IT architectures, IT management and telecommunications.
Newest articles

Properties of new materials for microchips
… can now be measured well. Reseachers of Delft University of Technology demonstrated measuring performance properties of ultrathin silicon membranes. Making ever smaller and more powerful chips requires new ultrathin…

Floating solar’s potential
… to support sustainable development by addressing climate, water, and energy goals holistically. A new study published this week in Nature Energy raises the potential for floating solar photovoltaics (FPV)…

Skyrmions move at record speeds
… a step towards the computing of the future. An international research team led by scientists from the CNRS1 has discovered that the magnetic nanobubbles2 known as skyrmions can be…





















