NIST releases new standard for semiconductor industry

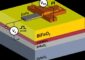
The 1-centimeter square coating, just 3 micrometers thick, is the first standard for the chemical composition of thin-film semiconductor alloys issued by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). Standard Reference Material (SRM) 2841 was requested by the compound semiconductor industry to help measure and control thin film composition as a basis for optimizing material and device properties.
The SRM can be used to calibrate equipment for making or analyzing these materials. Buyers are expected to include companies that grow or characterize thin films or use them to make devices, as well as government and university laboratories.
AlGaAs is used as a barrier material to increase conductivity in high-speed circuits for wireless communication; semiconductor lasers for optical disk drives, bar code scanning, xerography, and laser surgery; and light-emitting diodes for remote controls, traffic lights, and medical instruments. The NIST standard is expected to increase the accuracy of chemical characterization of AlGaAs films by an order of magnitude over the current state of the art.
Improved accuracy will reduce wasteful duplication of reference wafers, increase the free exchange of thin-film materials between vendors and their customers, and ultimately improve the accuracy of data on relationships between material composition and properties.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Power and Electrical Engineering
This topic covers issues related to energy generation, conversion, transportation and consumption and how the industry is addressing the challenge of energy efficiency in general.
innovations-report provides in-depth and informative reports and articles on subjects ranging from wind energy, fuel cell technology, solar energy, geothermal energy, petroleum, gas, nuclear engineering, alternative energy and energy efficiency to fusion, hydrogen and superconductor technologies.
Newest articles

“Nanostitches” enable lighter and tougher composite materials
In research that may lead to next-generation airplanes and spacecraft, MIT engineers used carbon nanotubes to prevent cracking in multilayered composites. To save on fuel and reduce aircraft emissions, engineers…

Trash to treasure
Researchers turn metal waste into catalyst for hydrogen. Scientists have found a way to transform metal waste into a highly efficient catalyst to make hydrogen from water, a discovery that…

Real-time detection of infectious disease viruses
… by searching for molecular fingerprinting. A research team consisting of Professor Kyoung-Duck Park and Taeyoung Moon and Huitae Joo, PhD candidates, from the Department of Physics at Pohang University…