Nanoscale model catalyst paves way toward atomic-level understanding

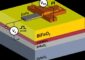
In an attempt to understand why ruthenium sulfide (RuS2) is so good at removing sulfur impurities from fuels, scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Brookhaven National Laboratory have succeeded in making a model of this catalyst — nanoparticles supported on an inert surface — which can be studied under laboratory conditions. “If we can understand why this catalyst is so active, we might be able to make it even better, or use what we learn to design other highly efficient catalysts,” said Tanhong Cai, one of the scientists who made the model.
Removing sulfur from fossil fuels such as oil and coal is mandated because the resulting fuels burn more cleanly and efficiently. One common way of achieving this is to add hydrogen in the presence of a catalyst to release hydrogen sulfide (H2S). Recently, RuS2 was found to be 100 times more active than the catalyst most commonly used for this “hydrodesulfurization” reaction. But studying the catalyst in action is nearly impossible because the reaction takes place at high temperatures and under extreme pressure.
The Brookhaven team has therefore created a model of the catalyst via a chemical reaction that deposits nanosized particles of RuS2 on a nonreactive gold surface. The small size of the particles maximizes the surface area available for the catalytic reaction to take place, and makes it ideal for analysis by classic surface chemistry techniques, such as scanning tunneling microscopy and x-ray photoemission spectroscopy. The entire model is being studied under well-defined ultrahigh vacuum conditions.
Cai will present a talk on the preparation and characterization of this model catalyst during the “Size-Selected Clusters on Surfaces, Divison of Physical Chemistry” session on Monday, September 8, 2003, at 4:30 p.m. in the Javits Convention Center, Room 1E10. This work was funded by the Division of Chemical Sciences, Office of Basic Energy Sciences at DOE’s Office of Science.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.bnl.gov/All latest news from the category: Power and Electrical Engineering
This topic covers issues related to energy generation, conversion, transportation and consumption and how the industry is addressing the challenge of energy efficiency in general.
innovations-report provides in-depth and informative reports and articles on subjects ranging from wind energy, fuel cell technology, solar energy, geothermal energy, petroleum, gas, nuclear engineering, alternative energy and energy efficiency to fusion, hydrogen and superconductor technologies.
Newest articles

Silicon Carbide Innovation Alliance to drive industrial-scale semiconductor work
Known for its ability to withstand extreme environments and high voltages, silicon carbide (SiC) is a semiconducting material made up of silicon and carbon atoms arranged into crystals that is…

New SPECT/CT technique shows impressive biomarker identification
…offers increased access for prostate cancer patients. A novel SPECT/CT acquisition method can accurately detect radiopharmaceutical biodistribution in a convenient manner for prostate cancer patients, opening the door for more…

How 3D printers can give robots a soft touch
Soft skin coverings and touch sensors have emerged as a promising feature for robots that are both safer and more intuitive for human interaction, but they are expensive and difficult…