Neuron and synapse-mimetic spintronics devices developed
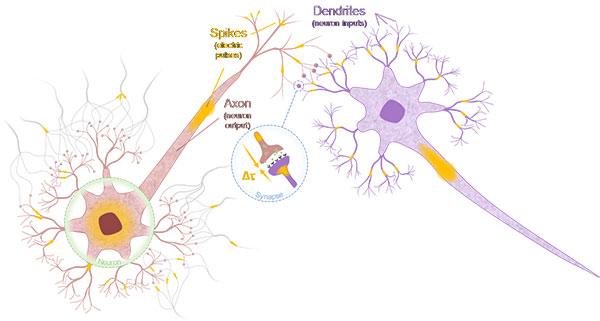
This is a neuron and synapse in biological neural network. Credit: Aleksandr Kurenkov and Shunsuke Fukami
Today's information society is built on digital computers that have evolved drastically for half a century and are capable of executing complicated tasks reliably.
The human brain, by contrast, operates under very limited power and is capable of executing complex tasks efficiently using an architecture that is vastly different from that of digital computers.
So the development of computing schemes or hardware inspired by the processing of information in the brain is of broad interest to scientists in fields ranging from physics, chemistry, material science and mathematics, to electronics and computer science.
In computing, there are various ways to implement the processing of information by a brain. Spiking neural network is a kind of implementation method which closely mimics the brain's architecture and temporal information processing.
Successful implementation of spiking neural network requires dedicated hardware with artificial neurons and synapses that are designed to exhibit the dynamics of biological neurons and synapses.
Here, the artificial neuron and synapse would ideally be made of the same material system and operated under the same working principle. However, this has been a challenging issue due to the fundamentally different nature of the neuron and synapse in biological neural networks.
The research group – which includes Professor Hideo Ohno (currently the university president), Associate Professor Shunsuke Fukami, Dr. Aleksandr Kurenkov and Professor Yoshihiko Horio – created an artificial neuron and synapse by using spintronics technology.
Spintronics is an academic field that aims to simultaneously use an electron's electric (charge) and magnetic (spin) properties.
The research group had previously developed a functional material system consisting of antiferromagnetic and ferromagnetic materials. This time, they prepared artificial neuronal and synaptic devices microfabricated from the material system, which demonstrated fundamental behavior of biological neuron and synapse – leaky integrate-and-fire and spike-timing-dependent plasticity, respectively – based on the same concept of spintronics.
The spiking neural network is known to be advantageous over today's artificial intelligence for the processing and prediction of temporal information. Expansion of the developed technology to unit-circuit, block and system levels is expected to lead to computers that can process time-varying information such as voice and video with a small amount of power or edge devices that have the an ability to adopt users and the environment through usage.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Power and Electrical Engineering
This topic covers issues related to energy generation, conversion, transportation and consumption and how the industry is addressing the challenge of energy efficiency in general.
innovations-report provides in-depth and informative reports and articles on subjects ranging from wind energy, fuel cell technology, solar energy, geothermal energy, petroleum, gas, nuclear engineering, alternative energy and energy efficiency to fusion, hydrogen and superconductor technologies.
Newest articles

Properties of new materials for microchips
… can now be measured well. Reseachers of Delft University of Technology demonstrated measuring performance properties of ultrathin silicon membranes. Making ever smaller and more powerful chips requires new ultrathin…

Floating solar’s potential
… to support sustainable development by addressing climate, water, and energy goals holistically. A new study published this week in Nature Energy raises the potential for floating solar photovoltaics (FPV)…

Skyrmions move at record speeds
… a step towards the computing of the future. An international research team led by scientists from the CNRS1 has discovered that the magnetic nanobubbles2 known as skyrmions can be…





















