Ben-Gurion University develops side-illuminated ultra-efficient solar cell designs
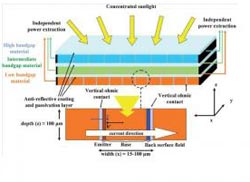
The new cell architecture (above) developed at the David Ben-Gurion National Solar Research Center at Ben-Gurion University of the Negev can exceed an ultra-efficient 40 percent conversion efficiency with intensities equal to 10,000 suns. When irradiated from the side, it generates solar conversion efficiencies that rival, and may eventually surpass, the most ultra-efficient photovolataics. This diagram is a schematic drawing of a 3-tier 6-terminal MBVJ solar cell. The number of tiers/materials is a design variable, and both the width (sub-cell dimension along the x-axis) and depth (sub-cell dimension along the z-axis) of each vertical junction need to be optimized.<br><br>Credit: Ben-Gurion University of the Negev<br>
Researchers at Ben-Gurion University of the Negev (BGU) have developed a radically new design for a concentrator solar cell that, when irradiated from the side, generates solar conversion efficiencies which rival, and may eventually surpass, the most ultra-efficient photovoltaics.
The new cell architecture developed at the David Ben-Gurion National Solar Research Center at BGU can exceed an ultra-efficient 40 percent conversion efficiency with intensities equal to 10,000 suns.
“Typically a concentrator solar cell comprises interdependent stacked materials connected in series, with significant associated fabrication difficulties and efficiency limitations,” explains Prof. Jeffrey Gordon, a member of the Department of Solar Energy and Environmental Physics at BGU's Jacob Blaustein Institutes for Desert Research.
“Our new designs for concentrator photovoltaic cells comprise multiple tiers of semiconductor materials that are totally independent, and overcome numerous challenges in compiling the elements of even the most efficient solar cells,” he says.
The BGU invention also demonstrates the distinctly new possibility of exploiting common materials, such as silicon, previously deemed unsuitable under highly concentrated solar radiation. Tailoring the cells to edge (side) illumination reduces the cell internal resistance to negligible levels. This increases the solar concentration levels at which cell efficiency peaks to up to 10,000 times ambient solar beam radiation, which is significantly higher than ever before.
“Our future depends on the development of alternative energies, and BGU is leading the way in this field,” explains Doron Krakow, executive vice president of American Associates, Ben- Gurion University of the Negev (AABGU). “Prof. Gordon and his colleagues in BGU's Energy Initiative continue to bring new innovations that will impact our world for the better.”
The new technology was recently detailed in a paper that appeared in Energy & Environmental Science.
American Associates, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev
American Associates, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev plays a vital role in sustaining David Ben-Gurion's vision, creating a world-class institution of education and research in the Israeli desert, nurturing the Negev community and sharing the University's expertise locally and around the globe. With some 20,000 students on campuses in Beer-Sheva, Sede Boqer and Eilat in Israel's southern desert, BGU is a university with a conscience, where the highest academic standards are integrated with community involvement, committed to sustainable development of the Negev. AABGU is headquartered in Manhattan and has nine regional offices throughout the U.S. For more information, visit www.aabgu.org.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.aabgu.org/All latest news from the category: Power and Electrical Engineering
This topic covers issues related to energy generation, conversion, transportation and consumption and how the industry is addressing the challenge of energy efficiency in general.
innovations-report provides in-depth and informative reports and articles on subjects ranging from wind energy, fuel cell technology, solar energy, geothermal energy, petroleum, gas, nuclear engineering, alternative energy and energy efficiency to fusion, hydrogen and superconductor technologies.
Newest articles

Silicon Carbide Innovation Alliance to drive industrial-scale semiconductor work
Known for its ability to withstand extreme environments and high voltages, silicon carbide (SiC) is a semiconducting material made up of silicon and carbon atoms arranged into crystals that is…

New SPECT/CT technique shows impressive biomarker identification
…offers increased access for prostate cancer patients. A novel SPECT/CT acquisition method can accurately detect radiopharmaceutical biodistribution in a convenient manner for prostate cancer patients, opening the door for more…

How 3D printers can give robots a soft touch
Soft skin coverings and touch sensors have emerged as a promising feature for robots that are both safer and more intuitive for human interaction, but they are expensive and difficult…