Gone with the wind–why the fast jet stream winds cannot contribute much renewable energy after all
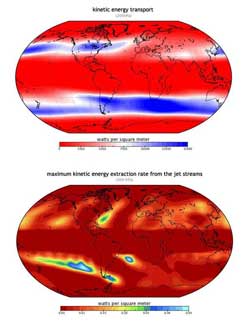
Graphics depicting the calculations for high kinetic energy transport (upper panel) versus maximum kinetic energy extraction rates (lower panel) from jet streams. Please note the units.<br>L. Miller / MPI-BGC Jena<br>
Taking into account that the high wind speeds result from the near absence of friction and not from a strong power source, Axel Kleidon and colleagues found that the maximum extractable energy from jet streams is approximately 200 times less than reported previously. Moreover, climate model simulations show that energy extraction by wind turbines from jet streams alters their flow, and this would profoundly impact the entire climate system of the planet.
Jet streams are regions of continuous wind speeds greater than 25 m/s that occur at altitudes of 7-16 km. Their high speeds seem to suggest an almost unlimited source of renewable energy that would only need airborne wind energy technology to utilize it. Claims that this potential energy source could “continuously power all civilization” sparked large investments into exploitation of this potential energy resource.
However, just like any other wind and weather system on Earth, jet streams are ultimately caused by the fact that the equatorial regions are heated more strongly by the sun than are polar regions. This difference in heating results in large differences in temperature and air pressure between the equator and the poles, which are the driving forces that set the atmosphere into motion and create wind. It is this differential heating that sets the upper limit on how much wind can be generated and how much of this could potentially be used as a renewable energy resource.
It is well known in meteorology that the high wind speeds of jet streams result from the near absence of friction. In technical terms, this fact is referred to in meteorology as “geostrophic flow”. This flow is governed by an accelerating force caused by pressure differences in the upper atmosphere, and the so-called Coriolis force arising from the Earth’s rotation. Because the geostrophic flow takes place in the upper atmosphere, far removed from the influence of the surface and at low air density, the slow-down by friction plays a very minor role. Hence, it takes only very little power to accelerate and sustain jet streams. “It is this low energy generation rate that ultimately limits the potential use of jet streams as a renewable energy resource”, says Dr. Axel Kleidon, head of the independent Max Planck Research Group ‘Biospheric Theory and Modelling’. Using this approach based on atmospheric energetics, Kleidon’s group used climate model simulations to calculate the maximum rate at which wind energy can be extracted from the global atmosphere. Their estimate of a maximum of 7.5 TW (1 TW = 10^12 W, a measure for power and energy consumption) is 200-times less than previously reported and could potentially account for merely about half of the global human energy demand of 17 TW in 2010.
Max Planck researchers also estimated the climatic consequences that would arise if jet stream wind power would be used as a renewable energy resource. As any wind turbine must add some drag to the flow to extract the energy of the wind and convert it into electricity, the balance of forces of the jet stream must also change as soon as energy is extracted. If 7.5 TW were extracted from jet streams as a renewable energy source, this would alter the natural balance of forces that shape the jet streams to such an extent that the driving atmospheric pressure gradient between the equator and the poles is depleted. “Such a disruption of jet stream flow would slow down the entire climate system. The atmosphere would generate 40 times less wind energy than what we would gain from the wind turbines”, explains Lee Miller, first author of the study. “This results in drastic changes in temperature and weather”.
The Max Planck study was published in the scientific journal Earth System Dynamics on November 29th, 2011. This study illustrates that fast winds are not always strong and powerful. Seemingly environmentally-friendly renewable energy technologies need to be carefully evaluated in the context of how the whole Earth system works.
Contact:
Dr. Axel Kleidon
Max Planck Institute for Biogeochemistry, Jena, Germany
Phone: +49 3641 576217
Fax: +49 3641 577200
Email: akleidon@bgc-jena.mpg.de
Background Information:
The Max Planck Institute for Biogeochemistry, founded in 1997, is dedicated to the study of long-term interactions among the biosphere, atmosphere, geosphere and the oceans. The research aims of the Institute include:
– quantifying the role of these interactions in the control of the Earth’s climate in a time of increasing anthropogenic impact;
– developing a quantitative and predictive understanding of the regulation of processes in ecosystems and their attendant biogeochemical cycles in the face of climate change;
– and investigating feedback mechanisms at the Earth’s surface that involve vegetation, atmospheric composition and climate. For more information see www.bgc-jena.mpg.de.
The independent Max Planck Research Group „Biospheric Theory and Modelling“, headed by Dr. Axel Kleidon, develops and uses theoretical approaches and numerical simulation models to investigate the role of the biota in driving the global geochemical cycles within the Earth system and how these affect the climatic conditions. It applies complex systems theories as well as thermodynamics to describe biotic effects on the environment. The group develops a range of simulation models to reproduce and explain the observed geographic variation of terrestrial vegetation, fluxes of energy, water, carbon, and other elements for the present-day and its past evolution. These approaches are used to evaluate the causes and consequences of human modifications to the Earth system (www.bgc-jena.mpg.de/bgc-theory).
Further information on the contents of this press release is available at www.bgc-jena.mpg.de/bgc-theory. Original data are published in:
– L.M. Miller, F. Gans, & A. Kleidon, 2011: Jet stream wind power as a renewable energy resource: little power, big impacts; Earth Syst. Dynam. 2, 201–212, 2011, doi: 10.5194/esd-2-201-2011.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

Properties of new materials for microchips
… can now be measured well. Reseachers of Delft University of Technology demonstrated measuring performance properties of ultrathin silicon membranes. Making ever smaller and more powerful chips requires new ultrathin…

Floating solar’s potential
… to support sustainable development by addressing climate, water, and energy goals holistically. A new study published this week in Nature Energy raises the potential for floating solar photovoltaics (FPV)…

Skyrmions move at record speeds
… a step towards the computing of the future. An international research team led by scientists from the CNRS1 has discovered that the magnetic nanobubbles2 known as skyrmions can be…




















