UMass Amherst Climate Researchers Find Evidence of Past Southern Hemisphere Rainfall Cycles Related to Antarctic Temperatures
The work by Stephen Burns and his doctoral student Lisa Kanner at UMass Amherst is reported in the current issue of ScienceXpress. Burns says, “The study also demonstrates that rainfall in the Southern Hemisphere of South America is, though to a lesser extent, also influenced by temperature changes in the Antarctic, which has not been previously observed.”
The last glacial period, from about 10,000 to about 120,000 years ago, saw North America and Western Europe covered in a thick continental ice sheet, the geoscientist points out. Yet climate was also highly unstable during the period, cycling every few thousand years between warm and cold, dry periods in the high northern latitudes. Temperatures could change by as much as 10 to 15 degrees Celsius.
Known as Dansgaard/Oeschger (D/O) cycles, these millennial-scale rapid climate events were first recognized in the Greenland ice cores, but have since been found throughout the Northern Hemisphere, Burns points out.
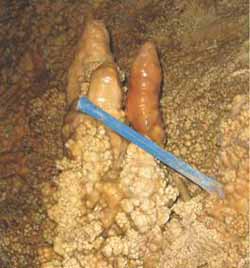
The UMass Amherst climate researcher is an expert in reading past climate data from the ratio of oxygen isotopes found in calcite in speleothems, another name for stalagmites, stalactites and other water-deposited cave features. Analyzing radioactive isotopes and stable oxygen isotopes in the calcite sampled from ancient cave formations can provide information on past rainfall over many thousands of years, Burns says.
He and Kanner used oxygen isotopic analyses from a 16-centimeter (about 6.3 inches) stalagmite recovered from a cave 2.4 miles (3,800 meters) above sea level in the Peruvian Andes for this study. The sample grew from 49,500 to 16,000 years ago, providing a 34,000-year-long record of rainfall changes in the Amazon Basin. Kanner and colleagues found that cold periods in the high Northern latitudes are associated with an increase in precipitation, the South American Summer Monsoon, in the Amazon Basin.
They found that cold periods in the Northern Hemisphere are associated with an increase in precipitation, the South American Summer Monsoon, in the Amazon Basin.
“This relationship is the exact opposite of changes in rainfall in the Northern Hemisphere tropics, where cold intervals result in a decrease in rainfall,” Burns says.
Revised chronology for several major climate events that took place in the last glacial period proposed in this study could lead to a better understanding of Antarctic warming during the same period and its relationship to warming the subtropical North Atlantic, the authors state.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.umass.eduAll latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

Silicon Carbide Innovation Alliance to drive industrial-scale semiconductor work
Known for its ability to withstand extreme environments and high voltages, silicon carbide (SiC) is a semiconducting material made up of silicon and carbon atoms arranged into crystals that is…

New SPECT/CT technique shows impressive biomarker identification
…offers increased access for prostate cancer patients. A novel SPECT/CT acquisition method can accurately detect radiopharmaceutical biodistribution in a convenient manner for prostate cancer patients, opening the door for more…

How 3D printers can give robots a soft touch
Soft skin coverings and touch sensors have emerged as a promising feature for robots that are both safer and more intuitive for human interaction, but they are expensive and difficult…




















