Tropical Storm Karina: Status quo on infrared satellite imagery
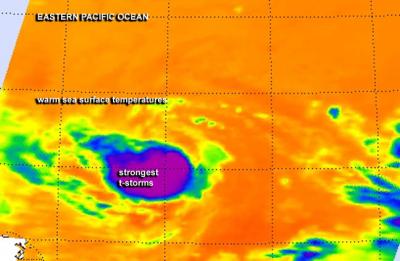
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical Storm Karina on August 18 at 6:23 a.m. EDT on Monday, August 18 and the AIRS instrument captured an infrared image. The image showed strong thunderstorms (purple) continued to circle the center. Credit: NASA JPL/Ed Olsen
Hurricane Karina formed on August 13, 2014 off the Mexican coast. The Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission or TRMM satellite passed directly above the center of intensifying tropical storm Karina on August 14, 2014 at 1927 UTC (3:27 p.m. EDT).
TRMM's Microwave Imager showed that storms near Karina's center were dropping rain at a rate of over 50mm (almost 2 inches) per hour. After that TRMM fly over, Karina was upgraded to a hurricane within a couple hours. However, in less than 24 hours, by August 15 at 5 a.m. EDT (0900 UTC), Karina weakened back to tropical storm status.
In the days that followed, Karina's cloud pattern didn't change much. Satellite data showed that strong thunderstorms still circle the center, especially on the northern edge.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical Storm Karina on August 18 at 6:23 a.m. EDT on Monday, August 18 and the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder or AIRS instrument captured infrared data on the storm's clouds.
Infrared data basically shows temperature, and the AIRS data showed strong thunderstorms with cloud top temperatures near -63F/-52C indicating they were high in the troposphere. The bulk of the strong thunderstorms continued to be pushed to the northern quadrant as a result of southerly wind shear.
At 11 a.m. EDT (1500 UTC) Karina's maximum sustained winds remain near 45 mph (75 kph). The center of Tropical Storm Karina was located near latitude 16.8 north and longitude 132.4 west, that's about 1,500 miles (2,415 km) east of Hilo, Hawaii.
Karina is moving toward the west-southwest near 9 mph (15 kph) and is expected to slow down. The estimated minimum central pressure is 1002 millibars.
NHC's forecaster Avila noted that “Karina has the chance to slightly strengthen since the circulation is moving over warmer waters and into weaker shear. By the end of the forecast period, the outflow from larger Tropical Depression 12-E to the northeast should induce stronger shear and prevent additional strengthening.”
Text credit: Rob Gutro
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.nasa.govAll latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

Peptides on Interstellar Ice
A research team led by Dr Serge Krasnokutski from the Astrophysics Laboratory at the Max Planck Institute for Astronomy at the University of Jena had already demonstrated that simple peptides…

A new look at the consequences of light pollution
GAME 2024 begins its experiments in eight countries. Can artificial light at night harm marine algae and impair their important functions for coastal ecosystems? This year’s project of the training…

Silicon Carbide Innovation Alliance to drive industrial-scale semiconductor work
Known for its ability to withstand extreme environments and high voltages, silicon carbide (SiC) is a semiconducting material made up of silicon and carbon atoms arranged into crystals that is…




















