Tropical Cyclone Helen headed for landfall in India
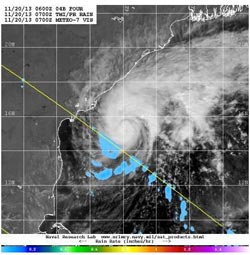
Visible/short wave infrared data from ESA's METEO-7 satellite and rainfall data from NASA's TRMM satellite was combined to create this image of Tropical Cyclone Helen on Nov. 20.<br><br>Credit: NRL/NASA/ESA<br>
On Nov. 20 at 1200 UTC/7 a.m. EST, Tropical Cyclone Helen had maximum sustained winds near 50 knots/57.5 mph/92.6 kph. It was centered near 15.5 north and 83.9 east, about 499 nautical miles/574.2 miles/924.1 km south-southwest of Calcutta, India. Helen was crawling to the northwest at 1 knot/1.1 mph/1.8 kph. A mid-level subtropical ridge (elongated area) of high pressure is expected to slowly build east of Helen and steer the storm on a more western track in the next day.
Current warnings are in effect for fishermen along the coasts of Andhra Pradesh, who are advised to return to shore.
Animated multispectral satellite showed a resurgence of deep convection over the low-level center of circulation. Satellite data also showed that the band of thunderstorms that appeared strong to the north has weakened and become fragmented. Visible/short wave infrared data from ESA's METEO-7 satellite and rainfall data from NASA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission or TRMM satellite was combined at the Naval Research Laboratory to create a composite image of the storm on Nov. 20. The image showed the clouds associated with Helen were mostly still over the open waters of the Arabian Sea, and that south of the center, light rainfall was occurring.
Helen is expected to intensify to 60 knots/69.0 mph/111.1 kph over the next two days and weaken before landfall. Helen is forecast to pass just south of the Yelichetladibba Palem and Nachugunta Reserved Forests in Andhra Pradesh, located in the coastal plain of Krishna Delta. Helen is expected to make landfall in the vicinity of Chinnaganjam in southeastern India.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.nasa.govAll latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

Properties of new materials for microchips
… can now be measured well. Reseachers of Delft University of Technology demonstrated measuring performance properties of ultrathin silicon membranes. Making ever smaller and more powerful chips requires new ultrathin…

Floating solar’s potential
… to support sustainable development by addressing climate, water, and energy goals holistically. A new study published this week in Nature Energy raises the potential for floating solar photovoltaics (FPV)…

Skyrmions move at record speeds
… a step towards the computing of the future. An international research team led by scientists from the CNRS1 has discovered that the magnetic nanobubbles2 known as skyrmions can be…




















