Study proves that magma chambers can be totally molten
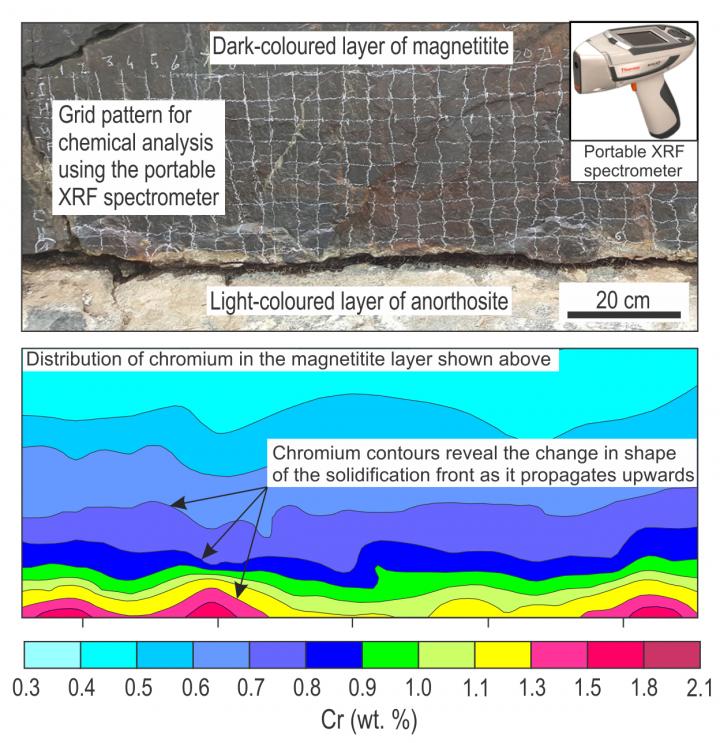
Photograph of a magnetitite layer from the Bushveld Complex and a chemical contour map showing the distribution of chromium within the layer after analysis with a portable XRF spectrometer. Credit: Wits University
Wits University (University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Africa) PhD student, Willem Kruger's study on the state of magma within plutonic magmatic systems in the Earth's crust has been published in the high impact journal, Nature Communications.
Working alongside his PhD supervisor, Professor Rais Latypov, from the Wits School of Geosciences, Kruger's paper shows that basaltic magma chambers may develop as large bodies of crystal-free melts in the Earth's crust.
This study challenges a recently-emerged paradigm that magma chambers are huge masses of crystal-rich mush – in other words, crystals with just a very small amount of melt.
Attempts to understand the processes that operate in magma chambers in our planet's crust is incredibly challenging as they are hidden from direct observations. Geologists must follow an indirect approach to study these features, such as examining their ancient fossilised remains that are exposed on Earth's surface after millions of years of erosion.
To examine the state of magma within a chamber is very demanding, as it requires the study of the very contact between the crystallising margins of magma bodies (also called solidification fronts) and their liquid interiors.
Difficulties in understanding the behaviour of solidification fronts can fortunately be overcome by studying a particularly fascinating rock type, called massive magnetitite, from the Bushveld Complex in South Africa.
“Magnetitite contains chromium that is an extremely sensitive indicator of magma chamber processes and can be used to study solidification fronts in extreme detail,” says Kruger.
“By mapping the distribution of chromium in magnetitite in the field we can observe the two-dimensional propagation patterns of solidification fronts on a scale never done before.”
Kruger and Latypov found that all evolved liquid is effectively removed from the solidification front of magnetitite as it propagates towards the chamber interior. “This is because of extremely effective compositional convection that occurs during the crystallisation of magnetite. The process results in the solidification front to propagate as almost a completely solid surface.” says Latypov.
This research shows that such powerful compositional convection may inhibit the formation of crystal-rich mushes in basaltic magma chambers.
There are many reasons to believe that this process is not unique to magnetitite layers of the Bushveld Complex but will likely operate in other rock types as well, for instance, in the Bushveld's economically important chromitite layers.
“Our results thus argue for the existence of large, liquid-dominated magma chambers hidden within the Earth's crust,” says Kruger.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

Properties of new materials for microchips
… can now be measured well. Reseachers of Delft University of Technology demonstrated measuring performance properties of ultrathin silicon membranes. Making ever smaller and more powerful chips requires new ultrathin…

Floating solar’s potential
… to support sustainable development by addressing climate, water, and energy goals holistically. A new study published this week in Nature Energy raises the potential for floating solar photovoltaics (FPV)…

Skyrmions move at record speeds
… a step towards the computing of the future. An international research team led by scientists from the CNRS1 has discovered that the magnetic nanobubbles2 known as skyrmions can be…




















