NASA sees the Tropical Cyclone Glenda away from land
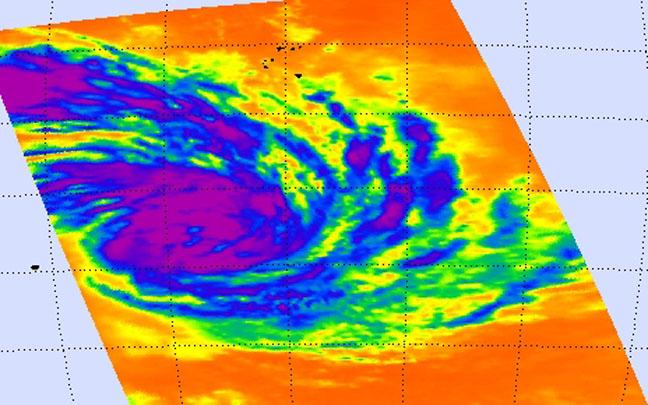
NASA's Aqua passed over Glenda on Feb. 25 at 06:47 UTC and saw strong thunderstorms with cloud top temperatures near -63F/-52C (purple) and a hint of an eye forming. Image Credit: NASA JPL, Ed Olsen
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Glenda and the AIRS instrument aboard captured infrared data on the storm on Feb. 25 at 06:47 UTC (1:47 A.M. EST). At that time, Glenda's maximum sustained winds were near 55 knots (63.2 mph/102 kph).
The infrared data measured cloud top temperatures and found the thunderstorms surrounding the center, were high, and powerful, with cloud top temperatures near -63F/-52C.
NASA research has shown that storms with cloud tops that cold have the potential to drop heavy rain. The infrared image also showed a hint of an eye forming in the center of circulation.
On Feb. 26 at 0900 UTC (4 a.m. EST), Tropical Cyclone Glenda's maximum sustained winds remained near 55 knots (63.2 mph/102 kph), but it is expected to strengthen.
It was centered near 20.7 south latitude and 67.6 east longitude, about 586 nautical miles (674 miles/1,085 km) east of Port Louis, Mauritius, far from land. Glenda was moving to the south-southwest at 7 knots (8 mph/13 kph).
The Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) noted “Animated multispectral satellite imagery depicts thinning convection with tightly-curved banding wrapping into a partially-exposed low-level circulation center.
Although the sea surface temperatures and ocean heat content are marginal, favorable upper-level conditions are expected to persist, allowing moderate Intensification over the next 36 hours.”
Glenda is expected to gradually intensify and then turn southeast and transition into an extra-tropical storm.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

Machine learning algorithm reveals long-theorized glass phase in crystal
Scientists have found evidence of an elusive, glassy phase of matter that emerges when a crystal’s perfect internal pattern is disrupted. X-ray technology and machine learning converge to shed light…

Mapping plant functional diversity from space
HKU ecologists revolutionize ecosystem monitoring with novel field-satellite integration. An international team of researchers, led by Professor Jin WU from the School of Biological Sciences at The University of Hong…

Inverters with constant full load capability
…enable an increase in the performance of electric drives. Overheating components significantly limit the performance of drivetrains in electric vehicles. Inverters in particular are subject to a high thermal load,…





















