NASA sees former tropical storm bow out 'Grace-fully'
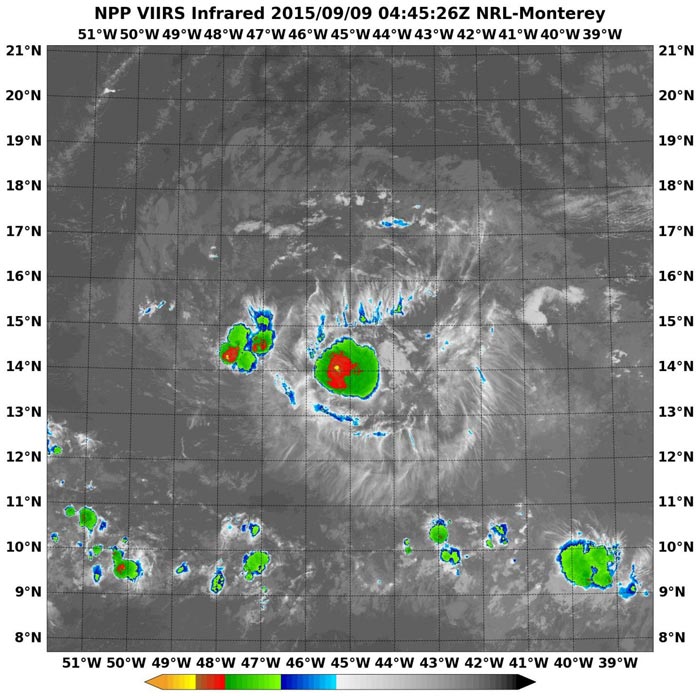
NASA-NOAA's Suomi satellite flew over Grace at 4:45 UTC (12:45 a.m. EDT) on Sept. 9 and the VIIRS instrument aboard captured this infrared image. Satellite data showed Grace no longer had a closed circulation. Credits: NRL/NASA/NOAA
NASA-NOAA's Suomi satellite flew over Grace at 4:45 UTC (12:45 a.m. EDT) on Sept. 9 and the VIIRS instrument aboard captured an infrared image of the storm. Satellite data showed Grace no longer had a closed circulation and is now an open wave.
At 11 a.m. EDT (1500 UTC), on September 9, the remnants of Grace were located near latitude 14.5 North and longitude 49.0 West. That puts Grace's remnants about 825 miles (1,325 km) east of the Lesser Antilles.
The remnants were moving toward the west near 18 mph (30 kph) and this general motion is expected to continue over the next couple of days. Maximum sustained winds were near 30 mph (45 kph) with higher gusts. The National Hurricane Center said that “little change in strength is expected over the next day or two.” The estimated minimum central pressure is 1008 millibars.
NHC Forecaster Pasch noted that “Data from the Rapidscat instrument onboard the International Space Station showed that there were no longer any westerly surface winds in Grace. This was confirmed by animation of high-resolution visible imagery that showed no westerly low-cloud motions.” Since Grace had opened up into a wave, the National Hurricane Center issued its final advisory.
Grace's remnant wave is expected to continue moving quickly to the west. NHC noted that the remnants could produce some gusty winds and showers over portions of the Lesser Antilles within a couple of days.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

Bringing bio-inspired robots to life
Nebraska researcher Eric Markvicka gets NSF CAREER Award to pursue manufacture of novel materials for soft robotics and stretchable electronics. Engineers are increasingly eager to develop robots that mimic the…

Bella moths use poison to attract mates
Scientists are closer to finding out how. Pyrrolizidine alkaloids are as bitter and toxic as they are hard to pronounce. They’re produced by several different types of plants and are…

AI tool creates ‘synthetic’ images of cells
…for enhanced microscopy analysis. Observing individual cells through microscopes can reveal a range of important cell biological phenomena that frequently play a role in human diseases, but the process of…





















