NASA satellite video and images show Dora become a major hurricane
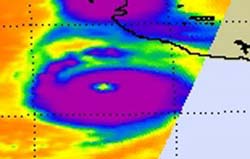
The AIRS instrument on NASA's Aqua satellite captured this infrared image of Hurricane Dora's cold cloud temperatures on July 21 at 09:05 UTC (5:05 a.m. EDT). The strongest thunderstorms and convection (purple) surround the very obvious, cloud-free eye. Credit: NASA/JPL, Ed Olsen<br>
Satellites provide a bird's eye view of a hurricane's eye, and NASA noticed Hurricane Dora's eye from several of them. Infrared imagery from NASA's Aqua satellite provided forecasters with a clear view of a cloud-free eye in hurricane Dora as she strengthens near Category 5 status today. Meanwhile the GOES-11 satellite captured a movie of Dora's intensification over the last two days that clearly shows a developing eye.
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument on NASA's Aqua satellite captured an infrared image of Hurricane Dora's cold cloud temperatures on July 21 at 09:05 UTC (5:05 a.m. EDT). The strongest thunderstorms and convection totally surrounded the very obvious, cloud-free eye.
The Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite called GOES-11 provides continuous visible and infrared imagery of the western U.S. and eastern Pacific Ocean basin from its position in space. GOES-11 images were compiled into a movie that runs from July 19 at 14:30 UTC (10:30 a.m. EDT) when Dora was a tropical storm, to July 21 at 14:30 UTC (10:30 a.m. EDT) now that Dora is a major hurricane.
GOES satellites are operated by NOAA, and the NASA GOES Project located at NASA Goddard creates images and compiled them into the video of the storm. The animation includes sped up infrared and visible frames of data that were captured every 15 minutes from the GOES-11 satellite and squeezed down to 26 seconds.
At 11 a.m. EDT on July 21, 2011 Dora's maximum sustained winds were near 155 mph (250 kmh), right on the brink of Category 5 hurricane status. Fortunately, Dora's center is remaining at sea, and will continue to remain at sea as it moves to the northwest near 12 mph (19 kmh). It is expected to continue in that direction for the next couple of days and slow down.
Dora was centered near 17.1N and 106.9W, about 240 miles (390 km) south-southwest of Cabo Corrientes, Mexico. Minimum central pressure is 929 millibars.
Dora is far enough off the coast so that there are no watches and warnings over land. However, Dora is sending large ocean swells against the beaches of western Mexico today. Those large, rough, ocean swells will affect the coast over the next couple of days, and will also begin affecting the southern Baja California coast.
The National Hurricane Center expects some weakening by tonight and a rapid weakening on Friday as Dora starts battling wind shear and moves into cooler waters.
NASA's Hurricane page: www.nasa.gov/hurricane; also at Twitter/NASAHurricane and on Facebook as NASA's Hurricane Web Page
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.nasa.govAll latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

Bringing bio-inspired robots to life
Nebraska researcher Eric Markvicka gets NSF CAREER Award to pursue manufacture of novel materials for soft robotics and stretchable electronics. Engineers are increasingly eager to develop robots that mimic the…

Bella moths use poison to attract mates
Scientists are closer to finding out how. Pyrrolizidine alkaloids are as bitter and toxic as they are hard to pronounce. They’re produced by several different types of plants and are…

AI tool creates ‘synthetic’ images of cells
…for enhanced microscopy analysis. Observing individual cells through microscopes can reveal a range of important cell biological phenomena that frequently play a role in human diseases, but the process of…





















