NASA's Aqua satellite sees remnants of Tropical Cyclone Tokage
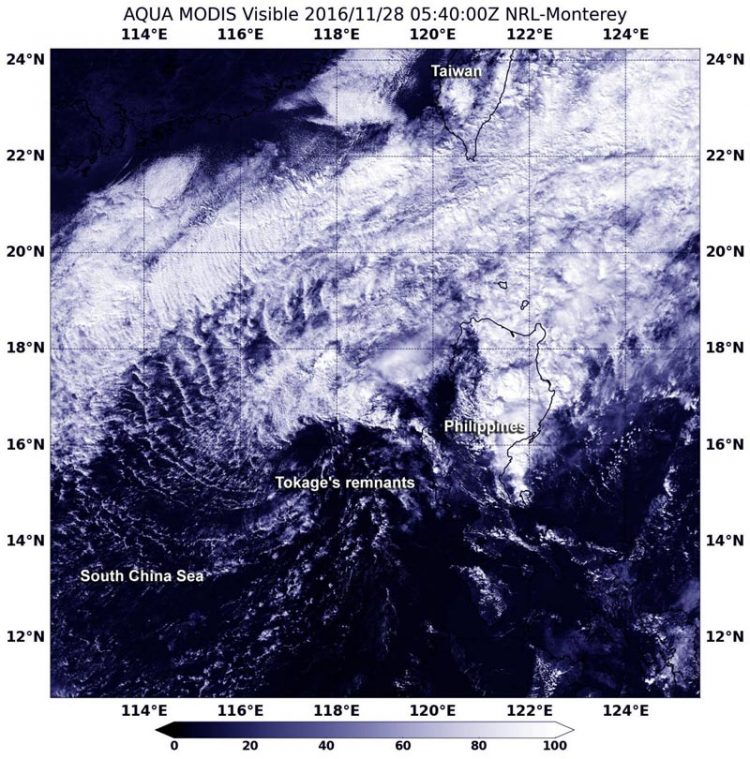
NASA's Aqua satellite captured a visible image of Tokage's remnants in the South China Sea on Nov. 28 at 1240 a.m. EST (540 UTC). Credit: NASA Goddard MODIS Rapid Response Team
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured a visible image of Tokage's remnants in the South China Sea on Nov. 28 at 1240 a.m. EST (540 UTC).
The image showed that the bulk of clouds associated with the remnants were pushed north of the center of circulation.
On Nov. 28 at 4 a.m. EST (0900 UTC), the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) issued their final warning on Tokage. At that time Tokage had maximum sustained winds near 28.7 mph (25 knots/46.3 kph) and they were weakening.
The storm was located near 16.3 degrees north latitude and 116.7 degrees east longitude, about 242 nautical miles west-northwest of Manila, Philippines. It was moving to the southwest at 19.5 mph (17 knots/31.4 kph).
JTWC noted that “animated multispectral satellite imagery reveals that the remnants of Tokage has embedded within the northeasterly cold surge which has caused it to accelerate southwestward and almost completely unravel.”
The remnants are expected to continue to move to the southwest and completely dissipate.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

Making diamonds at ambient pressure
Scientists develop novel liquid metal alloy system to synthesize diamond under moderate conditions. Did you know that 99% of synthetic diamonds are currently produced using high-pressure and high-temperature (HPHT) methods?[2]…

Eruption of mega-magnetic star lights up nearby galaxy
Thanks to ESA satellites, an international team including UNIGE researchers has detected a giant eruption coming from a magnetar, an extremely magnetic neutron star. While ESA’s satellite INTEGRAL was observing…

Solving the riddle of the sphingolipids in coronary artery disease
Weill Cornell Medicine investigators have uncovered a way to unleash in blood vessels the protective effects of a type of fat-related molecule known as a sphingolipid, suggesting a promising new…





















