NASA Adds Up Japan's Soaking Rains from Typhoon Phanfone
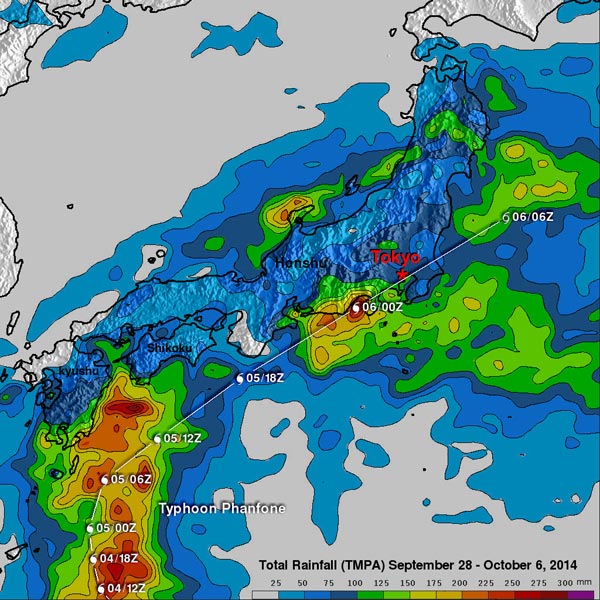
Typhoon Phanfone dropped rainfall over much of Japan but rainfall was particularly heavy near Phanfone's track along the southeastern coast of the islands. Phanfone's track and locations are shown overlaid in white. Image Credit: SSAI/NASA, Hal Pierce
The Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission or TRMM satellite has the ability to calculate rainfall rates within storms as it orbits around the Earth's tropics from space. TRMM data can also be used to create rainfall maps that show how much rain has fallen over given areas.
Phanfone was a powerful super typhoon with sustained wind speed estimated at 130 knots (150 mph) as it approached Japan but had weakened to a category one typhoon with sustained winds of about 70 knots (81 mph) as is passed near Tokyo.
The TRMM- based, near-real time Multi-satellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA) conducted at the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland has been measuring the distribution of precipitation over the tropics since TRMM's launch in 1997.
TMPA based rainfall totals were calculated for the period from September 28 to October 6, 2014 during which Phanfone formed east of Guam and traveled to Japan. The typhoon dropped rainfall over much of Japan but rainfall was particularly heavy near Phanfone's track along the southeastern coast of the islands.
The analysis indicated that Phanfone dropped the greatest amount of rainfall in central Japan west of Tokyo where rainfall totals greater than 275 mm (10.8 inches) were found. This analysis found some rainfall totals above 300 mm (11.8 inches) over the Pacific Ocean southeast of Japan.
Harold F. Pierce
SSAI/NASA Goddard Space Flight Center
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/phanfone-northwestern-pacific-ocean/All latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

Properties of new materials for microchips
… can now be measured well. Reseachers of Delft University of Technology demonstrated measuring performance properties of ultrathin silicon membranes. Making ever smaller and more powerful chips requires new ultrathin…

Floating solar’s potential
… to support sustainable development by addressing climate, water, and energy goals holistically. A new study published this week in Nature Energy raises the potential for floating solar photovoltaics (FPV)…

Skyrmions move at record speeds
… a step towards the computing of the future. An international research team led by scientists from the CNRS1 has discovered that the magnetic nanobubbles2 known as skyrmions can be…




















