Large volcanic eruption in Scotland may have contributed to prehistoric global warming
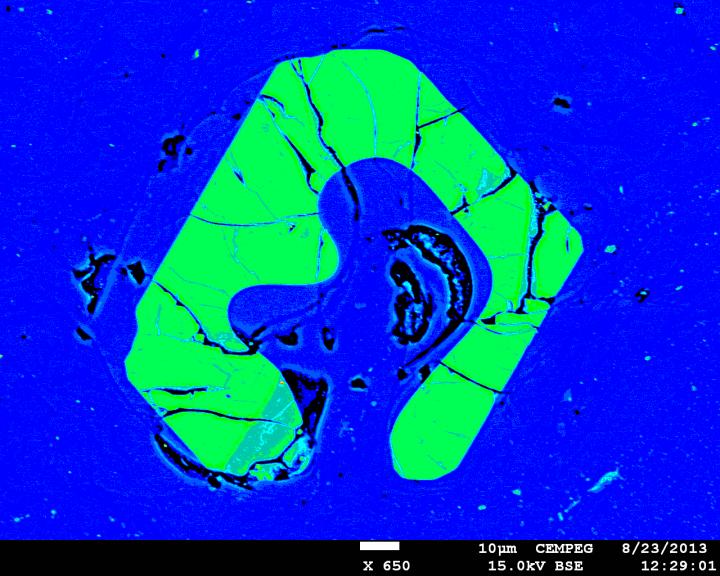
This is a false color electron-microscope image of a resorbed apatite crystal (green) in pitchstone glass (blue). The composition of the pitchstone glass and the characteristic mineral textures are identical in the studied pitchstone sites of the Sgùrr of Eigg and Òigh-sgeir, although over 30km apart, indicating a common origin, and thus a large and geographically widespread volcanic eruption. Credit: Valentin Troll Usage Restrictions: May only be published in connection to reports about the research by Valentin Troll et al.
Large explosive volcanic eruptions can have lasting effects on climate and have been held responsible for severe climate effects in Earth's history. One such event occurred around 56 million years ago when global temperatures increased by 5-8 °C.
This event has been named the Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum (PETM). The warm period was associated with volcanic activity in the North Atlantic region, especially in Greenland, the British Isles and the present day North Sea region. However, until now, no large-scale explosive eruptions had been confirmed in current-day Scotland.
A team of researchers at Uppsala University, Sweden, the Universities of Durham and St Andrews in the UK, and the Scottish Environmental Research Centre in Glasgow, now seem to have found a missing piece of the puzzle.
By studying volcanic rocks called pitchstones from islands more than 30 kilometres apart in the Inner Hebrides off the west coast of Scotland, the researchers have found plausible evidence of a major eruption from what is today the Isle of Skye.
The researchers used several different methods to compare the pitchstones recovered from the two sites (Sgùrr of Eigg and Òigh-sgeir) including isotope geochemistry. Samples from the two pitchstone outcrops display identical textures and compositions in all analyses, confirming that the two outcrops represent deposits of a single, massive and explosive volcanic eruption.
The researcher's geochemical data identify the Red Hills on Skye, around 40 kilometres to the North, as the most likely vent area for this large eruption. Using this vent location, a reconstruction estimates the eruption to have been similar in magnitude to the infamous Krakatoa eruption of 1883, one of the deadliest and most destructive volcanic events in recorded history.
Earth scientists have long thought that the Scottish sector of the North Atlantic Volcanic province did not see any large explosive eruptions at the time of the PETM.
This notion is now contradicted by the findings of the current study and the researchers conclude that large explosive volcanic events in the Scottish sector of the North Atlantic Volcanic Province were likely a major contributing factor to the climate disturbance of the PETM.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-35855-wAll latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

Superradiant atoms could push the boundaries of how precisely time can be measured
Superradiant atoms can help us measure time more precisely than ever. In a new study, researchers from the University of Copenhagen present a new method for measuring the time interval,…

Ion thermoelectric conversion devices for near room temperature
The electrode sheet of the thermoelectric device consists of ionic hydrogel, which is sandwiched between the electrodes to form, and the Prussian blue on the electrode undergoes a redox reaction…

Zap Energy achieves 37-million-degree temperatures in a compact device
New publication reports record electron temperatures for a small-scale, sheared-flow-stabilized Z-pinch fusion device. In the nine decades since humans first produced fusion reactions, only a few fusion technologies have demonstrated…





















