Los Alamos catalyst could jumpstart e-cars, green energy
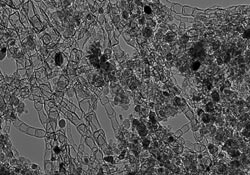
A high-resolution microscopic image of a new type of nanostructured-carbon-based catalyst developed at Los Alamos National Laboratory that could pave the way for reliable, economical next-generation batteries and alkaline fuel cells. (Photo credit: Los Alamos National Laboratory)<br>
Economical non-precious-metal catalyst capitalizes on carbon nanotubes
Los Alamos National Laboratory scientists have designed a new type of nanostructured-carbon-based catalyst that could pave the way for reliable, economical next-generation batteries and alkaline fuel cells, providing for practical use of wind- and solar-powered electricity, as well as enhanced hybrid electric vehicles.
In a paper appearing recently in Nature Communications, Los Alamos researchers Hoon T. Chung, Piotr Zelenay and Jong H. Won, the latter now at the Korea Basic Science Institute, describe a new type of nitrogen-doped carbon-nanotube catalyst. The new material has the highest oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) activity in alkaline media of any non-precious metal catalyst developed to date. This activity is critical for efficient storage of electrical energy.
The new catalyst doesn’t use precious metals such as platinum, which is more expensive per ounce than gold, yet it performs under certain conditions as effectively as many well-known and prohibitively expensive precious-metal catalysts developed for battery and fuel-cell use. Moreover, although the catalyst is based on nitrogen-containing carbon nanotubes, it does not require the tedious, toxic and costly processing that is usually required when converting such materials for catalytic use.
“These findings could help forge a path between nanostructured-carbon-based materials and alkaline fuel cells, metal-air batteries and certain electrolyzers,” said Zelenay. “A lithium-air secondary battery, potentially the most-promising metal-air battery known, has an energy storage potential that is 10 times greater than a state-of-the-art lithium-ion battery. Consequently, the new catalyst makes possible the creation of economical lithium-air batteries that could power electric vehicles, or provide efficient, reliable energy storage for intermittent sources of green energy, such as windmills or solar panels.”
The scientists developed an ingenious method for synthesizing the new catalyst using readily available chemicals that allow preparation of the material in a single step. They also demonstrated that the synthesis method can be scaled up to larger volumes and could also be used to prepare other carbon-nanotube-based materials.
The paper describing the breakthrough can be found here:
http://www.nature.com/ncomms/journal/v4/n5/full/ncomms2944.html
Project funding for the Los Alamos research came from the U.S. Department of Energy’s Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy (EERE) Office as well as from Los Alamos National Laboratory’s Technology Maturation Fund and Laboratory-Directed Research and Development program.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Automotive Engineering
Automotive Engineering highlights issues related to automobile manufacturing – including vehicle parts and accessories – and the environmental impact and safety of automotive products, production facilities and manufacturing processes.
innovations-report offers stimulating reports and articles on a variety of topics ranging from automobile fuel cells, hybrid technologies, energy saving vehicles and carbon particle filters to engine and brake technologies, driving safety and assistance systems.
Newest articles

Superradiant atoms could push the boundaries of how precisely time can be measured
Superradiant atoms can help us measure time more precisely than ever. In a new study, researchers from the University of Copenhagen present a new method for measuring the time interval,…

Ion thermoelectric conversion devices for near room temperature
The electrode sheet of the thermoelectric device consists of ionic hydrogel, which is sandwiched between the electrodes to form, and the Prussian blue on the electrode undergoes a redox reaction…

Zap Energy achieves 37-million-degree temperatures in a compact device
New publication reports record electron temperatures for a small-scale, sheared-flow-stabilized Z-pinch fusion device. In the nine decades since humans first produced fusion reactions, only a few fusion technologies have demonstrated…