Stanford Researcher Sheds New Light on the Mysteries of Spider Silk
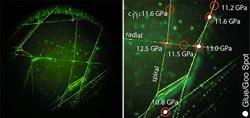
Stanford post-doctoral scholar Kristie Koski developed a clever way to measure the elastic response of intact spider webs using a century-old spectroscopy technique that does not require physical contact with the silk. At left is an intact web and, on the right, a detail demonstrating the pinpoint accuracy of Koski's system. The portion of the web examined is on the right-center of the photo on the left. (Photo and illustration courtesy of Kristie Koski, Stanford University.)<br>
By Andrew Myers
As fibers go, there’s never been anything quite like spider silk. Stretch it. Bend it. Soak it. Dry it out. Spider silk holds up. It is five times stronger than steel and can expand nearly a third greater than its original length and snap right back like new. Ounce-for-ounce spider silk is even stronger than Kevlar, the man-made fiber used in bulletproof vests.
It would be understandable to think that science knows all there is to know about the remarkable physics of spider silk, but the truth is far from that. Now, using a long-known-but-underutilized spectroscopy technique, a Stanford researcher has shed new light on the mysteries of spider silk.
On January 27, in a paper in the journal Nature Materials, post-doctoral scholar Kristie Koski described how she was able, for the first time, to non-invasively, non-destructively examine the mechanical properties of an intact, pristine spider web just as it was spun by the spider that created it. Koski is a researcher in the Yi Cui Group in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at Stanford University and the first author of the study. The work was performed when she was a post-doc under Professor Jeff Yarger at Arizona State University.
Stanford post-doctoral scholar Kristie Koski developed a clever way to measure the elastic response of intact spider webs using a century-old spectroscopy technique that does not require physical contact with the silk. At left is an intact web and, on the right, a detail demonstrating the pinpoint accuracy of Koski's system. The portion of the web examined is on the right-center of the photo on the left. (Photo and illustration courtesy of Kristie Koski, Stanford University.)
The complete elastic response of spider silk is described by five elastic constants that define how the web reacts to any possible combination of forces—pulling, twisting or shearing in any direction. All five have never been measured in a pristine spider web. At best, earlier studies have measured one or two of the five constants at a time and, even at that, only in isolated sections of a web. Structurally speaking, the old techniques are the equivalent of testing individual steel beams and cables and trying to extrapolate conclusions about the strength of a bridge.
Looking ahead, Koski believes that understanding the complete properties of a spider web exactly as it exists in nature is key to the engineering of new “bio-inspired” materials that not only mimic, but also improve upon nature.
“My goal is to study the nanostructure of silk to understand not just how spider silk behaves as it does, but also why it behaves in such remarkable ways in hopes of someday creating better man-made fibers,” said Koski.
Overlooked technique
The research was made possible by the use of a century-old-yet-overlooked measurement technique known as Brillouin spectroscopy. The technique shines laser light on the spider silks. The light produces sound waves in the silks, which, in turn, reflect some light back to the spectrometer. The researchers call the reflection “scattering.”
“It is a bit like plucking the string of a violin, only we never have to physically touch the string to play it,” said Koski.
The spectrometer measures small variations in the scattered light to ascertain the underlying tension of the silk being measured. The power of Brillouin scattering rests in the gentle way it gathers data enabling in situ measurements on spider webs, including mechanical properties at precise spots on the web such as silk intersections and glue spots.
Essentially, Koski and cohort have developed a non-invasive, non-destructive technique to measure the elasticity not just of individual strands of spider silk or even a few interconnected strands, as had those earlier studies, but of an entire intact spider web. Such exhaustive information was previously unobtainable with traditional stress–strain tests, which have to grip single strands or, at most, a few strands between two clamps to stretch them till they break.
“We don’t have to touch the web to measure it,” explained Koski.
The result is that Koski and collaborators are the first to quantify the complete linear elastic response of spider webs, testing for subtle variations in tension among discrete fibers, junctions, and glue spots for every type of deformation possible. It is a remarkable picture of the behavior of one of nature’s most intriguing structures.
Surprises
Among the team’s findings is that stiffness of a web is not uniform, but varies among isolated fibers, intersection points, and glue spots. For a structure formed supposedly of uniform spider silk, this was a bit of a surprise.
Evolutionarily, the researchers theorize this variation is advantageous to the spider in creating webs that are stiffer in some locations and more elastic in others. They think this might help the web withstand the elements and to better absorb the energy of captured prey.
Another surprise came when Koski looked at supercontraction. In high humidity—when it rains or in the morning dew—spider silk absorbs water, causing unrestrained fibers to shrink by as much as half, likely due to molecular disorganization caused by the water. It is a curious response for something so key to a spider’s survivability and it has raised some debate in the scientific community as to why nature would have favored supercontraction.
Scientists have posited three explanations for supercontraction. First, some think it is a mechanical constraint inherent in the molecular structure of silk, not an evolutionarily evolved phenomenon and that it has no bearing on the performance of a web. It’s just a fact of spider silk. The second theory is that supercontraction helps the spider tailor the silk as it is being spun to meet varying environmental and structural requirements. Or, lastly, that supercontraction helps tighten the web when it gets wet, preventing the heavy water droplets from dragging the web down and preventing the spider from catching any prey.
Until this paper, the last theory could not be tested because researchers had no way to probe complete webs. With their clever technique, Koski and team were able to measure the elastic response of silk during supercontraction. They found that the silk, which is essentially a matrix of restrained fibers, stiffens with 100% humidity, thus supporting the tightening web hypothesis.
The research also lends credence to the theory that supercontraction helps the spider tailor the properties of the silk during spinning by pulling and restraining the silk threads and adjusting the water content.
“The possibility of adjusting mechanical properties by simply adjusting water content is interesting from a bio-inspired mechanical structure perspective and could lead in interesting research directions as we try to invent new fibers,” said Koski.
Andrew Myers is associate director of communications for the Stanford University School of Engineering.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Materials Sciences
Materials management deals with the research, development, manufacturing and processing of raw and industrial materials. Key aspects here are biological and medical issues, which play an increasingly important role in this field.
innovations-report offers in-depth articles related to the development and application of materials and the structure and properties of new materials.
Newest articles

Peptides on Interstellar Ice
A research team led by Dr Serge Krasnokutski from the Astrophysics Laboratory at the Max Planck Institute for Astronomy at the University of Jena had already demonstrated that simple peptides…

A new look at the consequences of light pollution
GAME 2024 begins its experiments in eight countries. Can artificial light at night harm marine algae and impair their important functions for coastal ecosystems? This year’s project of the training…

Silicon Carbide Innovation Alliance to drive industrial-scale semiconductor work
Known for its ability to withstand extreme environments and high voltages, silicon carbide (SiC) is a semiconducting material made up of silicon and carbon atoms arranged into crystals that is…