Sponge-like 2D material with interesting electrical conductivity and magnetic properties
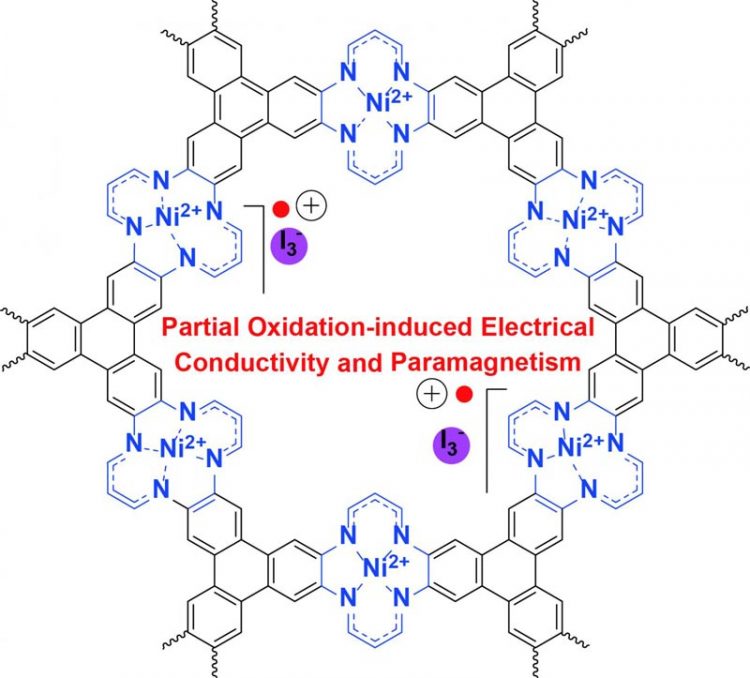
Chemical structure of iodine-doped Ni(II) tetraaza[14]annulene-linked MOF (NiTAA-MOF). While NiTAA-MOF is an insulator, the oxidized molecule acquires electrical conductivity and paramagnetism Credit: IBS
Chemists at the Center for Multidimensional Carbon Materials (CMCM), within the Institute for Basic Science (IBS, South Korea), have reported the synthesis of a novel type of 2D metal organic framework (MOF) with interesting electrical conductivity and magnetic properties.
Published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society, this new material may potentially contribute to optoelectronics, photovoltaics, (photo)electrocatalysis, and energy storage.
Also known as sponge-like or Swiss-cheese-like materials, MOFs are made of metal ions connected to organic ligands and are characterized by nano-sized holes. IBS researchers in collaboration with the School of Materials Science at the Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology (UNIST) designed and synthesized Ni(II) tetraaza[14]annulene-linked MOF (NiTAA-MOF), where the metal component is nickel and the nickel tetraaza[14]annulene molecules are used as MOF building blocks for the first time.
The researchers discovered that doping this MOF with iodine changes its conductivity and magnetism. Pristine NiTAA-MOF conducts poorly. It is actually an insulator with an electrical conductivity smaller than 10-10 Siemens per centimeter.
However, when it is chemically oxidized by iodine, the same measurement rises to 0.01 Siemens per centimeter (the larger this number, the better the conductor). This result shows the vital role of ligand oxidation in the electrical conductivity of some 2D MOFs, expanding the understanding of the origin of electrical conductivity in this type of MOFs.
In addition, the team checked how this material becomes magnetized in an applied magnetic field. Magnetization measurements performed by the researchers of the School of Materials Science showed that iodine-doped NiTAA-MOF is paramagnetic, that is it is weakly attracted by an external magnetic field, and becomes antiferromagnetic at very low temperatures. This means that it could become useful as a polarizing agent in dynamic nuclear polarization-nuclear magnetic resonance (DNP-NMR) that is used in experiments for material characterization.
The 2D MOF structure was also modeled through detailed calculations and analyzed by a variety of methods, such as X-ray diffraction, infrared, X-ray photoelectron, diffuse reflectance UV-vis, electron paramagnetic resonance, and Raman spectroscopies.
“Our work can contribute to the fundamental understanding of structure-property relationships in 2D electrically conductive MOFs, and may pave the way to develop new electrically conductive MOFs,” says Professor Ruoff, one of the corresponding authors of this study and UNIST professor. “Besides, the as-synthesized and iodine-doped NiTAA-MOF might be applicable in catalase mimics, catalysis, and energy storage.”
Media Contact
More Information:
http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/jacs.9b08601All latest news from the category: Materials Sciences
Materials management deals with the research, development, manufacturing and processing of raw and industrial materials. Key aspects here are biological and medical issues, which play an increasingly important role in this field.
innovations-report offers in-depth articles related to the development and application of materials and the structure and properties of new materials.
Newest articles

Superradiant atoms could push the boundaries of how precisely time can be measured
Superradiant atoms can help us measure time more precisely than ever. In a new study, researchers from the University of Copenhagen present a new method for measuring the time interval,…

Ion thermoelectric conversion devices for near room temperature
The electrode sheet of the thermoelectric device consists of ionic hydrogel, which is sandwiched between the electrodes to form, and the Prussian blue on the electrode undergoes a redox reaction…

Zap Energy achieves 37-million-degree temperatures in a compact device
New publication reports record electron temperatures for a small-scale, sheared-flow-stabilized Z-pinch fusion device. In the nine decades since humans first produced fusion reactions, only a few fusion technologies have demonstrated…





















